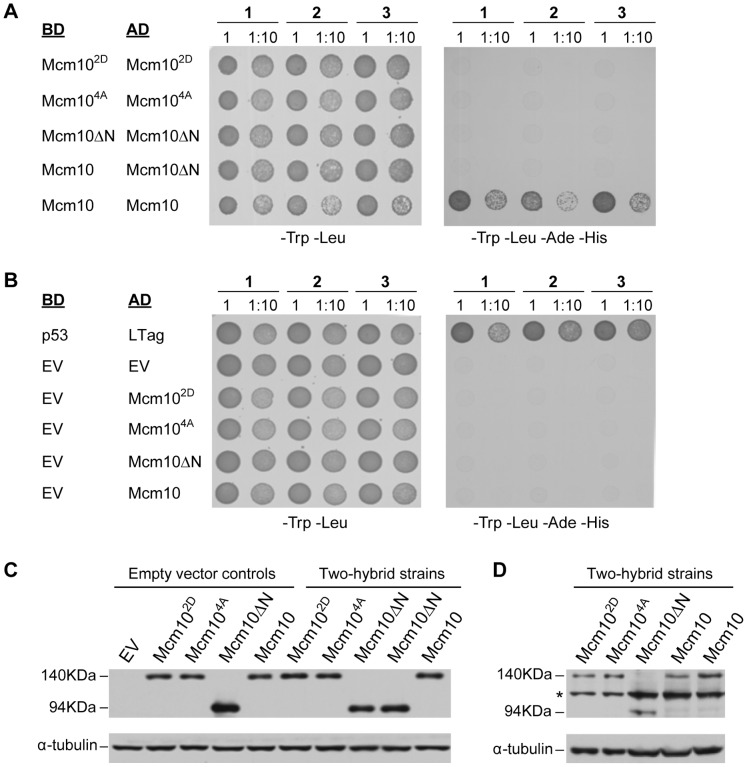
Figure 6. Coiled-coil mutations disrupt Mcm10 self-association.
(A, B) Three individual strains (1, 2, 3) harboring yeast two-hybrid plasmids that express the indicated proteins either as a fusion with the Gal4-binding domain (BD) or -activation domain (AD) were spotted onto drop-out plates lacking tryptophan and leucine (-Trp -Leu) or quadruple drop-out plates lacking tryptophan, leucine, adenine and histidine (-Trp -Leu -Ade -His). Cells were spotted at a number of 2×107 (1) or a 10-fold dilution (1∶10) for full-length Xenopus Mcm10, the L104D/L108D mutant (Mcm102D), the L104A/L108A/M115A/L118A mutant (Mcm104A), and the NTD deletion mutant spanning residues 230–860 (Mcm10ΔN). p53 and large T-antigen (LTag) served as a positive control, EV indicates empty vector controls. (C) Western blot showing wild-type and mutant xMcm10 protein expression in representative strains. Gal4-AD fusions were detected by a HA-specific antibody. Strains carrying empty vector controls, or Gal4-AD fusion genes and Gal4-BD empty vectors are shown on the left (Empty vector controls). Strains expressing pair-wise combinations of the Gal4-AD and Gal4-BD fusion genes as indicated in panels A and B are shown on the right (Two-hybrid strains). Full-length xMcm10 and the 2D and 4A mutants ran at an approximate size of 140 kDa, whereas the truncated form of xMcm10 ran at an approximate size of 94 kDa. Tubulin served as a loading control. (D) Gal4-BD fusions were detected by a Myc-specific antibody. Extracts from the identical two-hybrid strains shown in (C) were loaded in the same order. The asterisk denotes a non-specific band.