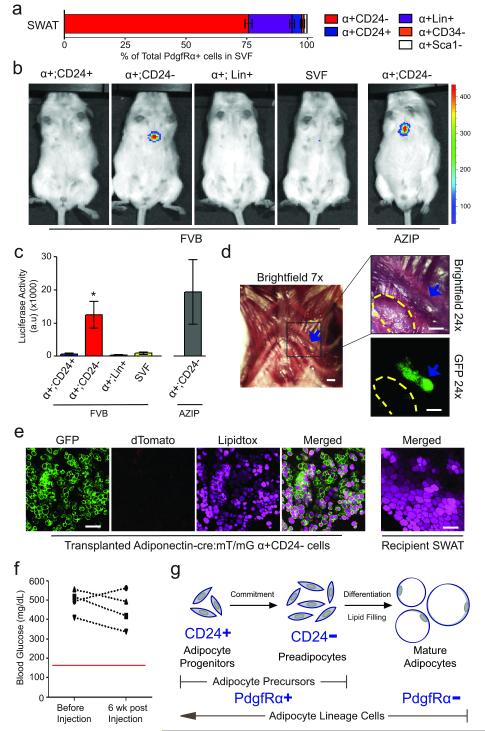
Figure 4.
CD24− cells are further committed to an adipogenic fate. (a) Breakdown of PdgfRα+ (α+) SVF into subpopulations. Flow cytometry plots and percentages are shown in Supplemental Figure 2b. α+:CD24−, α+:CD24+, and α+:Sca1− are Lin−:CD29+:CD34+. α+:CD34− are Lin−:CD29+. (b) Luminescence in 12-week old FVBN/J or A-Zip mice at 6 weeks post subcutaneous sternum transplantation of indicated FACS isolated populations from 6-week old leptin-luciferase BAC transgenic mice. 50,000 cells were transplanted per experiment. (c) Quantification of luminescence from (b) (n=5 for α+:CD24+ and α+:Lin+ transplants into FVB; n=10 for α+:CD24− and SVF transplants into FVB; n=4 for α+:CD24− transplants into AZIP. *p<.05, error bars represent S.E.M.). (d) Brightfield and fluorescent images of tissue formed 6 weeks post subcutaneous sternum transplantation of 2×105 Adiponectin-Cre:mT/mG α+:CD24− cells. Blue arrow indicates tissue formed from transplanted cells. Yellow dashes outline a small piece of recipient SWAT placed on top of sternum as a negative imaging control. Scale bars represent 1 mm. (e) Representative confocal images of Lipidtox stained tissues from (d). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (f) Blood glucose measurement of A-Zip mice before and 6 weeks post subcutaneous sternum transplantation of 50,000 α+CD24− as shown in (b) and (c). (g) A model of in vivo adipogenesis.