Figure 3. SIRT4 deacetylates MCD.
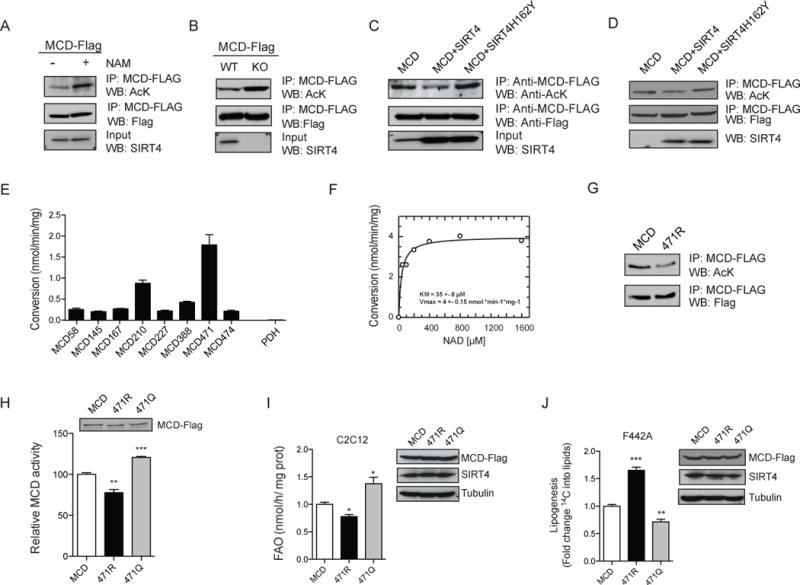
(A) MCD acetylation was measured in WT immortalized MEFs before or after treatment with NAM. FLAG-tagged MCD was stably overexpressed in WT MEFs treated with (+) or without (−) NAM and immunoprecipitated using antibodies against FLAG. MCD acetylation levels were assessed with antibodies against acetyl-lysine (AcK). (B) MCD acetylation was assessed using WT and SIRT4 KO MEFs as described for panel A. (C) MCD acetylation was measured in C2C12 cells stably overexpressing FLAG-tagged MCD and SIRT4 or SIRT4H162Y. After immunoprecipitation of MCD with anti-FLAG antibodies, acetylation was measured as for panel A. (D) In vitro deacetylation assay was performed using immunopurified MCD and SIRT4. FLAG-MCD was immunoprecipitated from MEFs and incubated with FLAG-SIRT4 and FLAG-SIRT4H162Y immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells and MCD acetylation status assessed by Western blot. (E) Recombinant SIRT4 was incubated with synthesized acetylated peptides of MCD and peptide deacetylation was assessed using mass spectrometry. Acetylated peptide from pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) was included as a negative control (n=3). (F) Acetylated peptide was incubated with SIRT4 and NAD+ concentrations were varied as indicated. Peptide deacetylation levels were analyzed by LC-MS. (G) Constructs encoding MCD, MCD K471R or MCD K471Q were expressed in HEK 293T cells and MCD activity was measured (n=4). (H–I) Retrovirus used to generate stable C2C12 (H) and F442A (I) cell lines overexpressing MCD, MCD K471R or MCD K471Q where FAO rates and lipogenesis were assessed (n=3). In each panel, data represent mean ± SEM. (*) p < 0.05; (**) p < 0.01, (***) p < 0.001. See also Figure S2 and S6.
