Abstract
Hereditary angioedema (HAE), an auto-somal dominant disorder characterized by attacks of episodic edema is associated with decreased functional levels of the C1 esterase inhibitor. Approximately 85% of patients have lowered antigen levels of a normal inhibitor protein. 15% of patients have normal or elevated antigenic levels of functionless protein. We have examined the response to danazol therapy of patients with the variant HAE phenotypes possessing the abnormal protein in an effort to determine if these patients possess a normal structural C1 inhibitor allele. Four patients with a variant HAE phenotype were treated successfully with danazol. In two patients, distinguished by the presence of a functionless, albumin-bound, C1 inhibitor (phenotype 2), phenotypic analysis of the danazol response by bidirectional immunoelectrophoresis revealed the appearance of the normal C1 inhibitor gene product during danazol therapy. This relatively cathodal C1 inhibitor peak appears in conjunction with the development of nearly normal functional activity. All of the functional C1 inhibitory activity which appeared in the phenotype 2 treatment serum was associated with the electrophoretically normal inhibitor. This normal protein could be separated from the functionless inhibitor protein by immunoadsorption and molecular sieve chromatography. Danazol therapy of the two patients with an electrophoretically normal, functionless C1 inhibitor (phenotype 3) also resulted in a clinical remission associated with development of a significant increment in functional serum C1 inhibitory activity and C1 inhibitor protein. These findings demonstrate that these two HAE phenotypic variants are heterozygous for the normal serum C1 inhibitor, a finding which was not apparent before phenotypic analysis of this serum during danazol therapy. These data provide strong evidence for a basic similarity between the common form of HAE and its phenotypic variants. They also suggest that a structural gene lesion may result in the abnormalities of serum C1 inhibitor function and disease expression in all three of these HAE phenotypes.
Full text
PDF


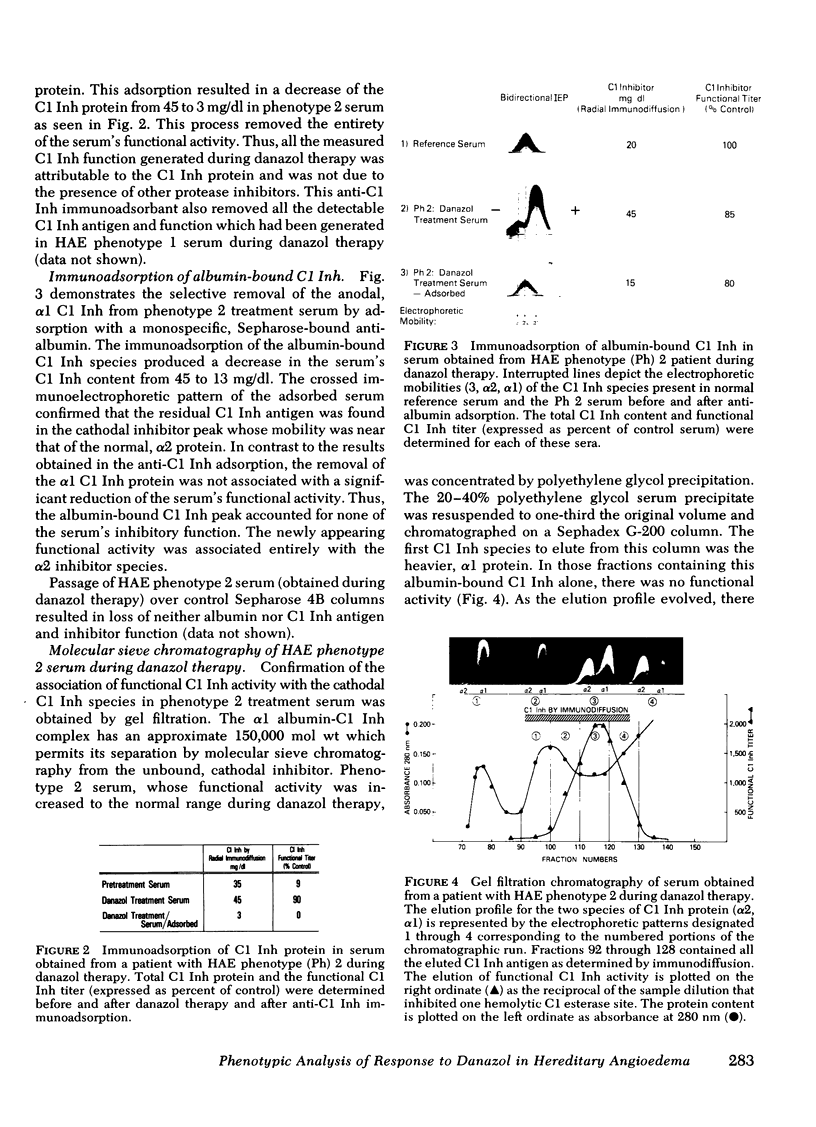



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., ROSEN F. S. ACTION OF COMPLEMENT IN HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: THE ROLE OF C'1-ESTERASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2204–2213. doi: 10.1172/JCI105094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Davis F. B., Charache P. Long-term therapy of hereditary angioedema (HAE). Preventive management with fluoxymesterone and oxymetholone in severely affected males and females. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1974 Dec;135(6):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Ratnoff O. D., Dias Da Silva W., Rosen F. S. Permeability-increasing activity in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma. II. Mechanism of formation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):642–653. doi: 10.1172/JCI106022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Gelfand J. A., Atkinson J. P. Hereditary angioedema: the clinical syndrome and its management. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):580–593. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Sherins R. J., Alling D. W., Frank M. M. Treatment of hereditary angioedema with danazol. Reversal of clinical and biochemical abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 23;295(26):1444–1448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612232952602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The stoichiometric measurement of the serum inhibition of the first component of complement by the inhibition of immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1154–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kueppers F., Black L. F. Alpha1-antitrypsin and its deficiency. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Aug;110(2):176–194. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Mårtensson U. C1 inactivator protein complexed with albumin in plasma from a patient with angioneurotic edema. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Apr;1(2):146–149. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Farley C. H., DeSimone P. A. Familial thrombosis due to antithrombin 3 deficiency. Blood. 1974 Feb;43(2):219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F. S., PENSKY J., DONALDSON V., CHARACHE P. HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: TWO GENETIC VARIANTS. Science. 1965 May 14;148(3672):957–958. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3672.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Alper C. A., Pensky J., Klemperer M. R., Donaldson V. H. Genetically determined heterogeneity of the C1 esterase inhibitor in patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2143–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI106708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokeir M. H. The genetics of hereditary angioedema: a hypothesis. Clin Genet. 1973 Jun;4(6):494–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Audran R. The isolation of IgG from mammalian sera with the aid of caprylic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]