Table 2.
The average AUROC for each of the methods on banana data
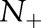 |
LR | OC-SVM | OC-SVM (Neg) | TC-SVM | TC-SVM (CS) | OP-SVM | OP-SVM (CS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 (0.18%) | 0.513 (±0.004) | 0.857 (±0.005) | 0.863 (±0.006) | 0.867 (±0.007) | 0.912 (±0.003) | 0.929 (±0.002) | 0.925 (±0.003) |
| 10 (0.37%) | 0.520 (±0.004) | 0.865 (±0.004) | 0.878 (±0.003) | 0.877 (±0.004) | 0.912 (±0.002) | 0.932 (±0.002) | 0.926 (±0.003) |
| 15 (0.55%) | 0.517 (±0.004) | 0.869 (±0.004) | 0.883 (±0.003) | 0.898 (±0.003) | 0.914 (±0.002) | 0.935 (±0.001) | 0.932 (±0.002) |
| 20 (0.74%) | 0.517 (±0.004) | 0.872 (±0.004) | 0.885 (±0.002) | 0.904 (±0.003) | 0.917 (±0.002) | 0.935 (±0.001) | 0.933 (±0.001) |
| 25 (0.92%) | 0.521 (±0.004) | 0.877 (±0.003) | 0.884 (±0.002) | 0.909 (±0.003) | 0.923 (±0.002) | 0.935 (±0.001) | 0.933 (±0.002) |
| 30 (1.11%) | 0.525 (±0.004) | 0.875 (±0.003) | 0.887 (±0.002) | 0.919 (±0.003) | 0.925 (±0.002) | 0.936 (±0.001) | 0.934 (±0.002) |
| 35 (1.29%) | 0.523 (±0.005) | 0.875 (±0.003) | 0.886 (±0.002) | 0.927 (±0.002) | 0.931 (±0.002) | 0.936 (±0.001) | 0.935 (±0.001) |
| 40 (1.48%) | 0.527 (±0.004) | 0.876 (±0.003) | 0.889 (±0.002) | 0.930 (±0.002) | 0.940 (±0.002) | 0.937 (±0.001) | 0.937 (±0.001) |
| 45 (1.66%) | 0.530 (±0.004) | 0.876 (±0.003) | 0.890 (±0.002) | 0.937 (±0.002) | 0.945 (±0.002) | 0.938 (±0.001) | 0.939 (±0.001) |
| 50 (1.85%) | 0.528 (±0.004) | 0.876 (±0.003) | 0.887 (±0.002) | 0.938 (±0.002) | 0.944 (±0.002) | 0.937 (±0.001) | 0.938 (±0.002) |
The proportion of positive examples in training sets was varied from 0.18% to 1.85%. The best AUROC values are shown in boldface, with the second best shown in italics.
AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; LR, logistic regression; OC-SVM, one-class support vector machine classification; OP-SVM, one-plus-class support vector machine; TC-SVM, two-class support vector machine classification.
