Fig. 7. Loss of one copy of par-1 or the Rac genes enhances adult wing defects caused by reduced Hh signaling.
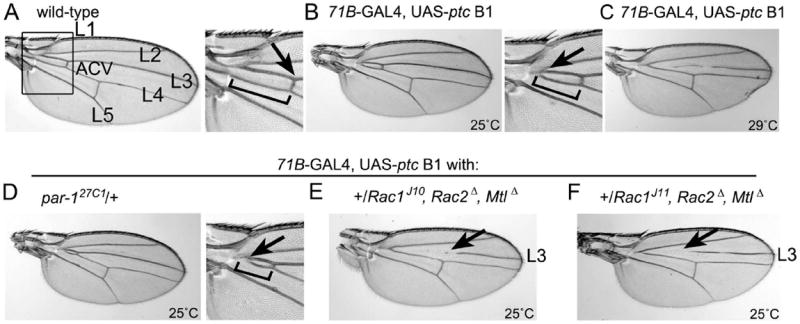
(A) Wild-type wing in which the longitudinal veins L1-L5 and anterior crossvein (ACV) are indicated (left panel). The boxed region is expanded (right panel) to show the normal length of veins L3-L4 (bracket) on the proximal side of the ACV (arrow) located between L3 and L4. (B) Reduced Hh signaling via overexpression of ptc at 25°C results in mild wing phenotypes (Johnson et al., 1995); reduced length of the L3-L4 longitudinal veins proximal to the ACV (bracket) and fusion of the proximal end (arrow) are indicated. (C) Severe wing vein phenotype caused by overexpression of ptc at 29°C. (D) Enhancement of the mild ptc overexpression vein fusion phenotype (arrow, bracket) upon loss of one copy of par-1 at 25°C. (E, F) Removal of one copy of all three Rac genes, using two different Rac1 alleles, at 25°C strongly enhances the mild ptc overexpression phenotype. The ACV and portions of the L3 longitudinal vein (arrows) are eliminated, which phenocopies severe ptc overexpression at 29°C (compare to [C]). Note that overexpression of ptc reduces overall wing size (Johnson et al., 1995).
