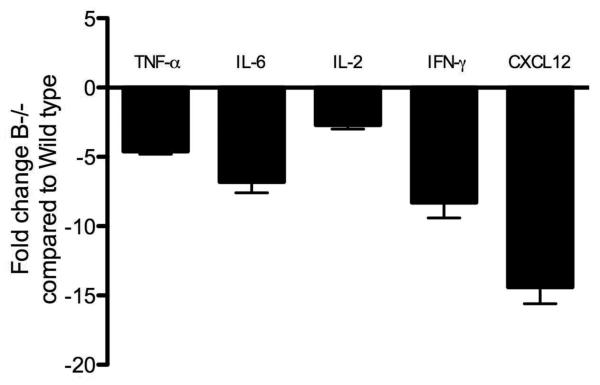
Figure 3. Significant reduction in the pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in B cell deficient mice following anti-MHC Ab administration.
B6.129S2-Igh-6tm1Cgn/J (B−/−) or control C57BL/6 mice (Wild type) were treated with anti-MHC class I Abs day 1, 2 and 3. We analyzed the expression levels of cytokines and chemokines in the lungs by quantitative real-time PCR on Day 4. There was a significant reduction in the expression of TNF-α (4.6 folds), IL-6 (6.8 folds), IL-2 (2.7 folds), IFN-γ (8.3 folds) and CXCL12 (14.4 folds) in the lungs of B cell deficient mice when compared to the wild type controls. Data representative of mean ± SD fold change observed, with 5 mice per group.