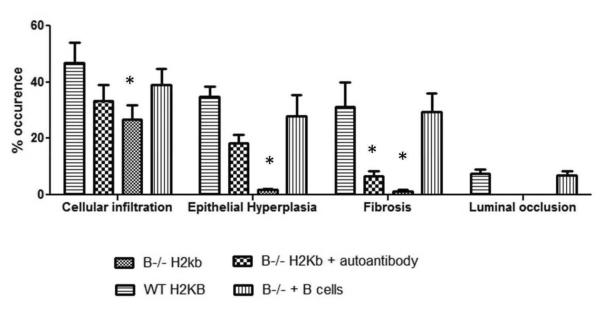
Figure 8. Morphometric analysis showing reduced cellular infiltration, epithelial hyperplasia, fibrosis and luminal occlusion in B cell KO mice and in B cell KO mice with passive transfer of auto-Abs.
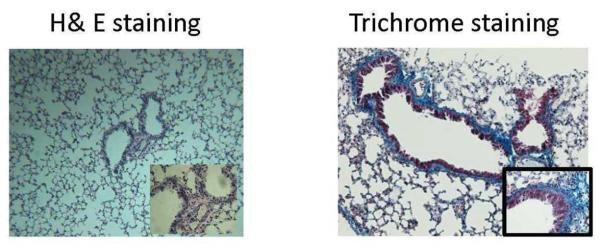
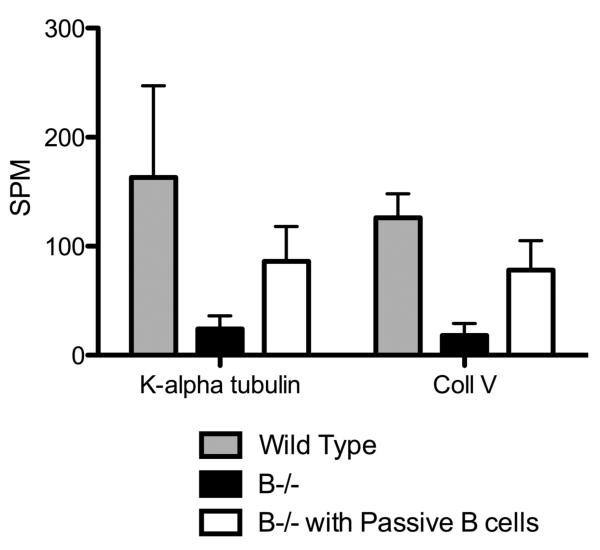
A: B6.129S2-Igh-6tm1Cgn/J (B cell KO), control C57BL/6 (wild type), B cell KO mice with passive transfer of 2.5×106 B cells (purified from splenocytes using B cell enrichment kit, Miltenyi Biotech) and B cell KO mice with passive transfer of 250ng each of Abs to ColV and K-α1T (on day 1) were treated with anti-MHC class I (anti-H2kb Abs on day 1, 2, 3, 6 and weekly thereafter (5 mice in each group). The lungs were harvested on day 30. Formalin preserved tissues were sectioned randomly and analyzed by H&E and Masson's trichrome staining. Images were captured and sections morphometric analysis performed using Optimas software (Media cybernetics). B-cell KO mice demonstrated significantly lesser bronchioles and vessels with cellular infiltration and epithelial hyperplasia. On passively transferring auto-Abs, only some bronchioles and vessels had epithelial hyperplasia or cellular infiltration with absence of any fibrosis when compared to wild type mice or B cell KO mice with passively transferred B cells. % occurrence refers to the percentage of bronchioles/vessels with cellular infiltration, epithelial hyperplasia, fibrosis or luminal occlusion per total number of bronchioles/vessels visualized in the lung sections. Data is mean ± SD of that observed in 5 mice per group. B: H&E and trichrome staining of the lungs. C: ELISPOT analysis of the lung infiltrating T cells specific for K-α1T and ColV in wild type mice, B−/− mice and B−/− mice passively transferred B cells from wild type mice.