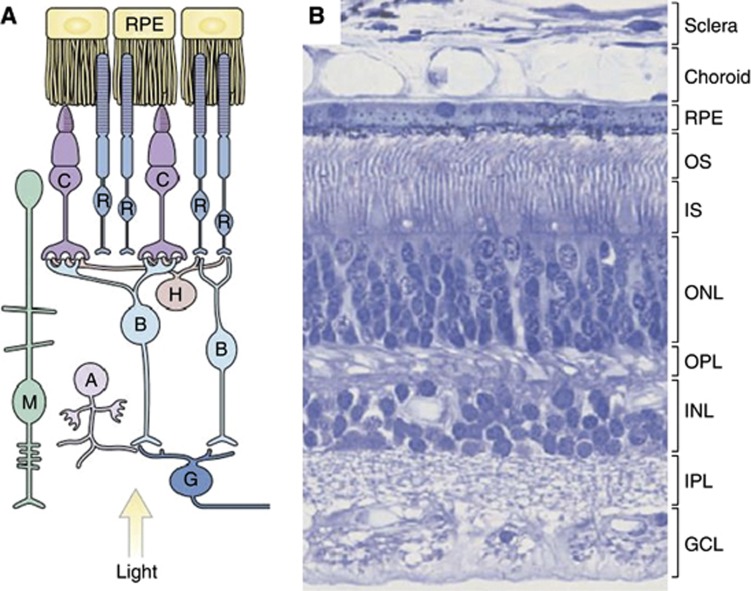
Figure 1.
The human retina. (A) Organisation of the retina. (B) A H&E-stained section of the retina shows the outer and inner segments (OS, IS) of rod and cone photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor nuclei form the outer nuclear layer (ONL). Nuclei of bipolar, amacrine, horizontal and Müller glial cells form the inner nuclear layer (INL), and the nuclei of ganglion cells form the ganglion cell layer (GCL). The outer plexiform layer (OPL) contains the processes and synaptic terminals of photoreceptors, horizontal and bipolar cells. The inner plexiform layer (IPL) contains the processes and synaptic terminals of bipolar, amacrine and ganglion cells. The processes of Müller glial cells fill all the retinal space not occupied by neurons and blood vessels. (Reproduced from Sung and Chuang (2010)). Abbreviations: A, amacrine cell; B, bipolar cell; C, cone; G, ganglion cell; H, horizontal cell; M, Müller glial cell; R, rod; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.