Figure 5. IL-20R signaling sumoylates C/EBPβ, a transcriptional regulator of IL-1β.
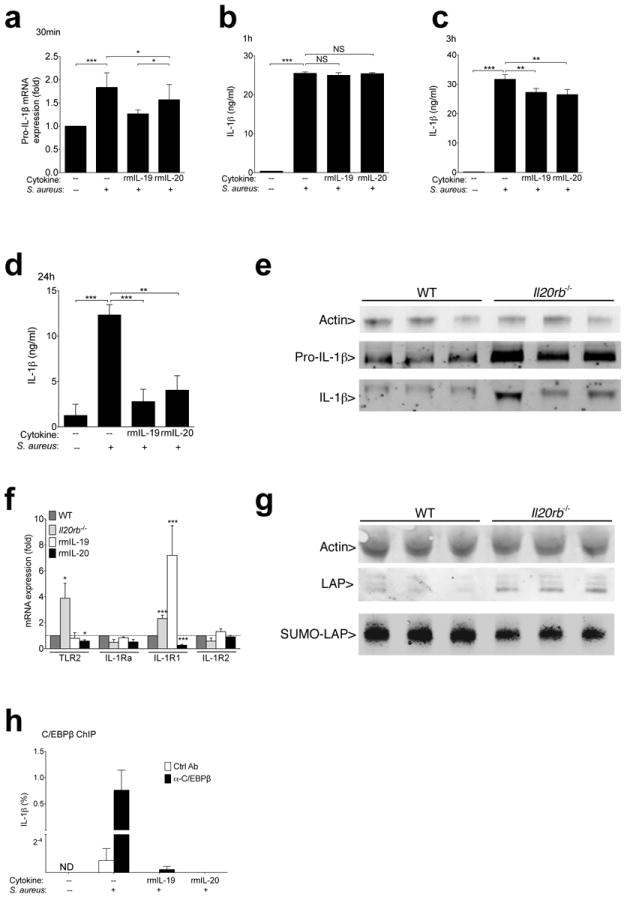
(a) Pro-IL-1β mRNA expression in PAM 2-12 mouse keratinocytes cultured for 30 minutes with 50:1 ratio of S. aureus (Wood46 strain bioparticles) with or without 15 minute pre-exposure to indicated cytokines. (b-d) IL-1β detected by ELISA in supernatants of PAM 2-12 keratinocytes after 1 hour (b), 3 hours (c), or 24 hours (d) of S. aureus exposure (Wood46 strain bioparticles). (e) Pro-IL-1β (31 kDa) and IL-1β (17 kDa) detected by immunoblot of wild type and Il-20rb−/− primary keratinocyte lysates after 24 hours of live MRSA USA300 exposure. Each lane shows lysates derived from an individual mouse. To optimally visualize actin (42 kDa), samples were run on a separate gel loaded with less protein. (f) Wild type (WT), Il20rb−/−, or recombinant cytokine-treated (rmIL-19 or rmIL-20) wild type mice were infected with MRSA. Tissue was harvested, and transcript levels were compared to wild type mice two hours after infection. (g) Immunoblot of actin (42 kDa) and C/EBPβ (LAP) (35-39 kDa) in primary keratinocyte lysates after 30 minutes of exposure to live MRSA. Anti-SUMO2/3 immunoprecipitates from the same cell lysates were run on a separate gel loaded with higher protein concentrations to detect SUMO associated LAP (SUMO-LAP). Each lane represents an individual mouse. (h) Relative chromatin binding of CEBP/β at IL-1β promoter in PAM 2-12 keratinocytes after incubation with or without MRSA and recombinant cytokines. Binding is displayed as percent of input DNA after immunoprecipitation with CEBP/β or isotype control antibody. Data shown are representative of 2-5 independent experiments, each using at least 3 mice per group (e-g) or replicate cell cultures (a-d, h), and displayed as mean + s.e.m. ND, not detected. NS, not significant.
