Figure 6. Recombinant IL-1β rescues IL-20R cytokine-induced susceptibility to S. aureus.
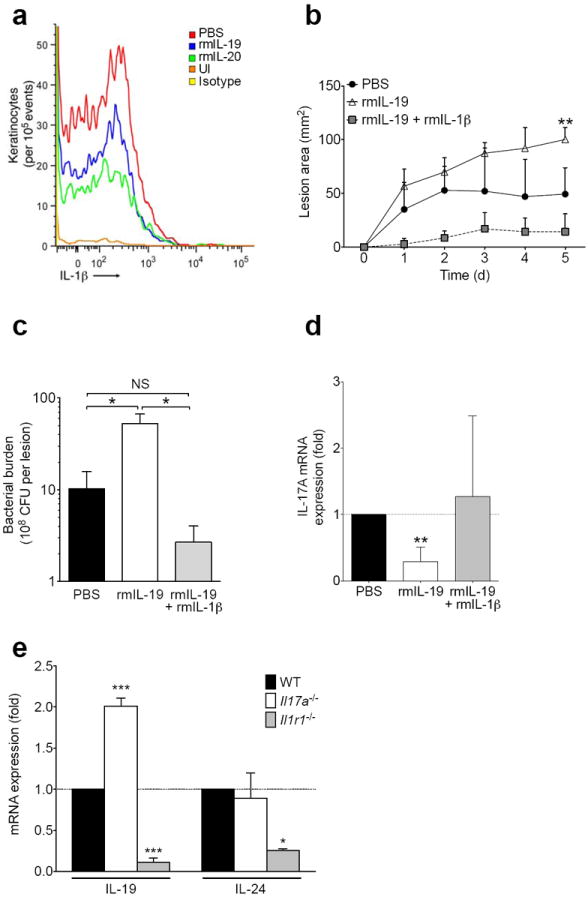
(a) IL-1β expression in live CD104+ keratinocytes detected by flow cytometry of single cell suspensions from infected skin tissue three days after MRSA infection with or without (PBS) recombinant murine cytokine (rmIL-19, rmIL-20) treatment. Staining of uninfected skin (UI) and staining with isotype control antibody also shown. (b-d) Wild type mice were inoculated with MRSA in PBS, rmIL-19, or rmIL-19 + rmIL-1β and assessed for lesion size (b), bacterial burden (c), and IL-17A mRNA (d). (e) IL-19 and IL-24 mRNA expression in Il17a−/−and Il1r1−/− mice, normalized to wild type (WT) mice, six days after infection with MRSA. Data shown are representative of 2-3 independent experiments, using at least 3-5 mice per group each time, and displayed as mean + s.e.m.
