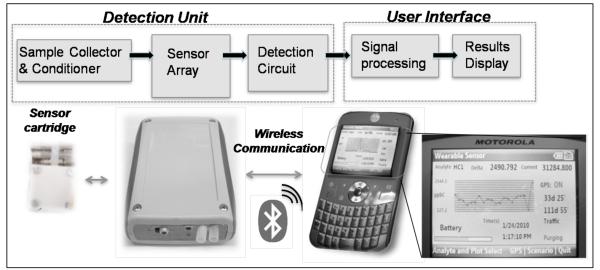
Fig. 1.
Wearable monitor for total hydrocarbons and total acids. Top: Block diagram of functions performed by the detection unit and user interface. Bottom: Pictures of the plug-and-play sensor cartridge with a tuning fork array; the wireless hand-held unit wirelessly connected to a Motorola Q9h smart phone, which processes the data, stores and displays the detection results. Bottom right: picture of the cell phone display, showing a real-time concentration plot (ppb levels vs. time), GPS data, active displayed sensing element (hydrocarbon sensor 1: HC1), active application (traffic) and valve status (purging).