Figure 1.
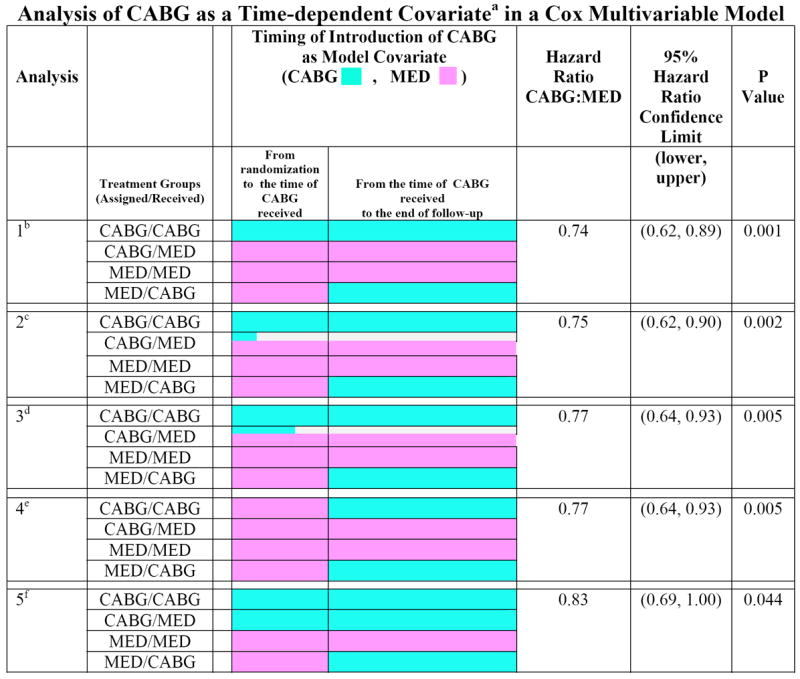
Time-dependent covariate Cox multivariable analysis of CABG vs. MED.
a. A numeric (0, 1) time-dependent covariate was created in the Cox model to indicate whether and when a patient received CABG, with the format of 1 = CABG and 0= MED. This variable allows an assessment of the CABG treatment effect to begin at the time that a patient actually received CABG. A patient is counted in the MED group until the CABG variable is switched to 1.
b. Analysis 1 has the CABG variable initially set to 1 for all patients who were assigned to CABG and actually received CABG. For patients assigned to MED who crossed over to CABG, the CABG variable is started as 0 and set to 1 at the time of the crossover. For all other patients (i.e., those assigned to MED who received MED, and assigned to CABG but did not receive CABG), the time-dependent CABG variable remains as 0 in the Cox model.
c. Analysis 2 is the same as Analysis 1 except that early deaths in patients randomized to CABG are handled differently. In this analysis, patients who were assigned to CABG but died within 30 days after randomization without receiving CABG are counted as CABG=1. These patients are not counted as MED patients (as in Analysis 1) even though they never received CABG. Thus, these early deaths are credited to the CABG arm.
d. Analysis 3 is the same as Analysis 2 except that patients who died within 60 days after randomization before receiving CABG are all counted as CABG=1.
e. Analysis 4 has the CABG variable started as 0 (MED) for all 1212 Hypothesis 1 patients. For patients who received CABG treatment, the CABG variable is set to 1 on the day of surgery.
f. Analysis 5 has the CABG variable started as 1 for all patients who were randomized to CABG regardless of whether they ever received the CABG. For all the other patients (i.e., MED patients), the CABG variable is started as 0 and switched to 1 at the time of CABG for any patients who crossed over from MED to CABG.
