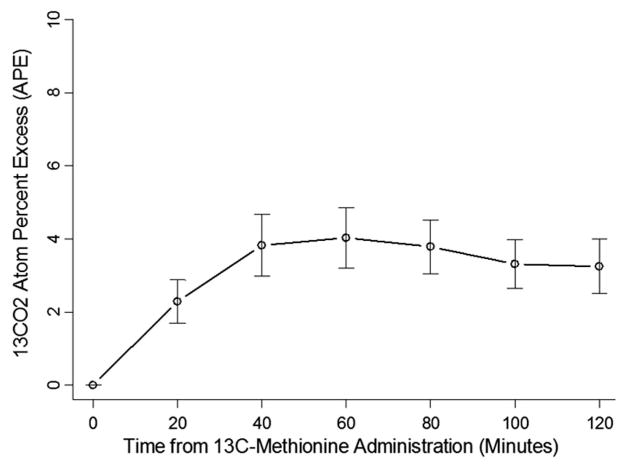
Figure 1.
13 CO2 atoms percent excess (APE), of the 27 patients. The APE is an expression of stable isotope enrichment within the total CO2 pool and reflects 13C-methionine tracer oxidation in the liver. It can be defined as: APE = tracer/(tracer + tracee) × 100, where the tracer (in this case, 13CO2), is a compound that is chemically and functionally identical to the naturally occurring compound of interest, the tracee (12CO2) (40). As time from 13C-methionine administration increases, the appearance of 13CO2 increases, which is in accordance with expectations because as discussed in the introduction, metabolism of 13C-methionine is anticipated to result in production of 13CO2.