Figure 2.
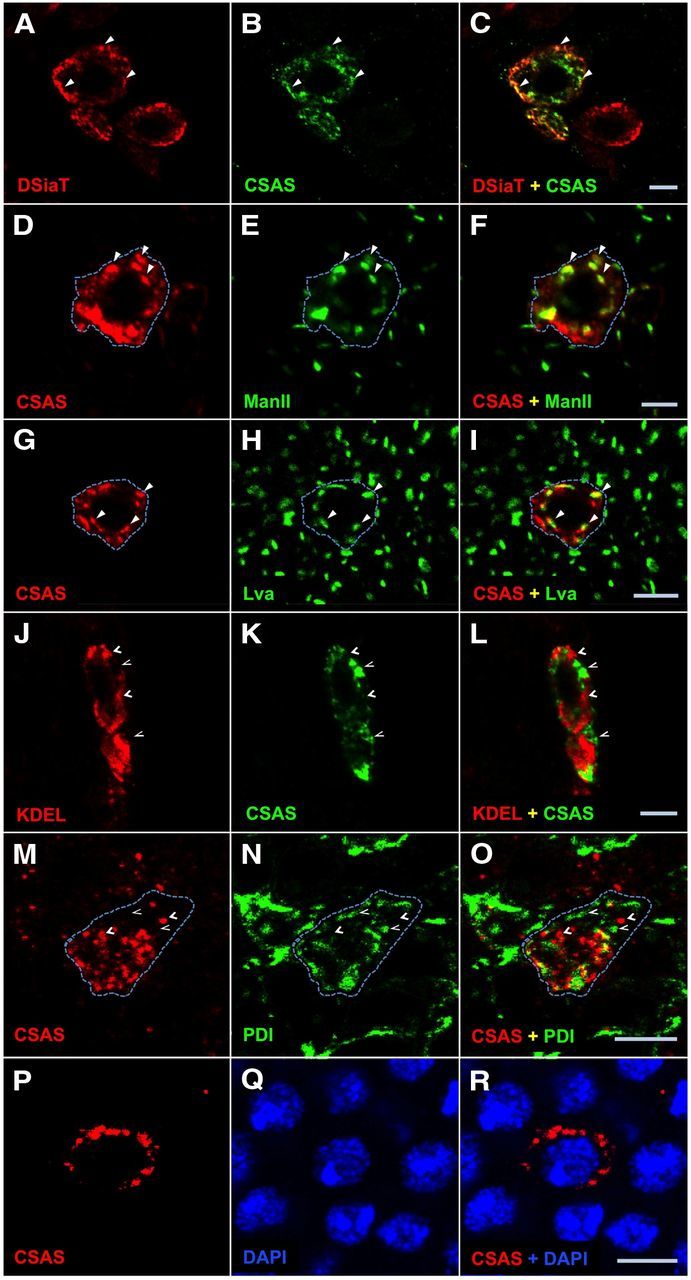
CSAS protein localizes to the secretory pathway compartment in Drosophila neurons. A–C, CSAS is largely colocalized with sialyltransferase (DSiaT) within the cell. A, DSiaT (red). B, CSAS (green). C, Overlay of A and B. D–F, Simultaneous detection of CSAS (D, red) and ManII (E, green) reveals significant colocalization of these proteins. F, Overlay of D and E. G–I, CSAS (G, red) shows substantial colocalization with Lva (H, green). I, Overlay of G and H. J–L, Codetection of KDEL (J, red) and CSAS (K, green) shows a minimal overlap between their localizations. L, Overlay of J and K. M–O, CSAS (J, red) and protein disulfide-isomerase (PDI; K, green) are minimally colocalized within the cell. O is the overlay of M and N. P–R, CSAS (J, red) and DAPI (K, green) have no colocalization within the cell. R is the overlay of P and Q. Solid and open arrowheads indicate examples of colocalization and the absence of colocalization, respectively. Dashed line helps visualize an approximate area occupied by a single cell with CSAS expression. Images represent confocal sections of third instar larval brains. CSAS-FLAG, ManII, and DSiaT proteins were expressed in the brain using C155 neuronal driver. PDI-GFP is a protein-trap that expresses endogeneous PDI tagged with GFP. Scale bars, 5 μm.
