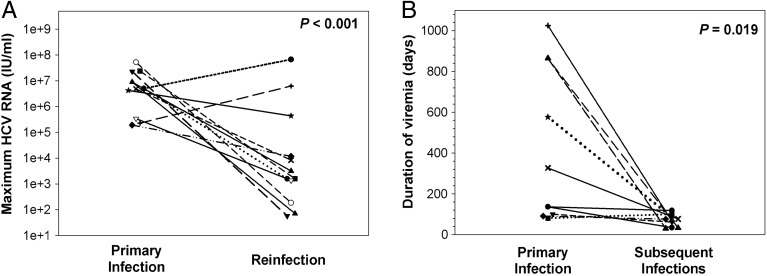
Figure 1.
Clearance of a primary infection attenuates the infection kinetics of subsequent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in injection drug users. A, Maximum HCV RNA concentrations (IU/mL) detected in serum samples obtained during primary and subsequent infections in subjects with sufficient follow-up after the detection of a reinfection. Triangles represent maximum viremia detected in reinfection-persistent subjects. The maximum viremia in each subject during initial infection and reinfection is connected by a line. Median maximum HCV RNA concentration of reinfections was significantly lower than that of primary infections (P < .001). B, Duration of viremia (days) during primary infections and subsequent infections in reinfection-cleared subjects. The duration of initial and reinfection viremia in each subject is connected by a line. The duration of viremia during reinfection was significantly lower than in primary infection (P = .019). Reprinted from Osburn et al [26] with permission. Abbreviation: HCV, hepatitis C virus.