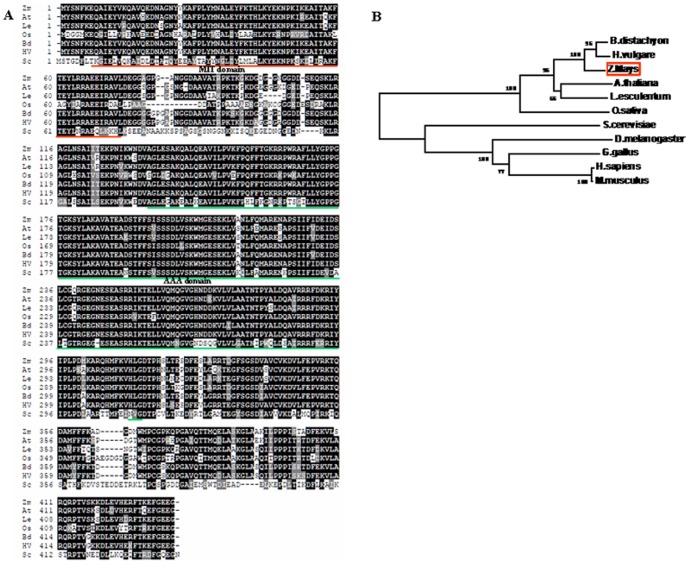
Figure 1. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of SKD1 proteins from Zea Mays and other species.
A An alignment is shown for the deduced amino acid sequence of SKD1s from Zea Mays (Zm), Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Lycopersicon esculentum (Le), Oryza sativa (Os), Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), Hordeum vulgare (Hv) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc). The numbers on the left indicate the amino acid position. Identical residues in all these proteins are shown in a black background. Dashes indicated gaps introduced for optimal alignment. The putative MIT and AAA domains are underlined with a thick red line and a thick green line, respectively. B Phylogenetic tree based on SKD1 protein sequences from yeast, plants, and animals. The bootstrap values shown were calculated based on 500 replications. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method. Z.mays, AY105155; A.thaliana, At2g27600; L.esculentum, AK324437; O.sativa, AF499028; B.distachyon, LOC100837561; H.vulgare, AK359160; D.melanogaster, NP_573258; G.gallus, AJ720732; H.sapiens, AF038960; M.musculus, NP_033216; S.cerevisiae, NP_015499.