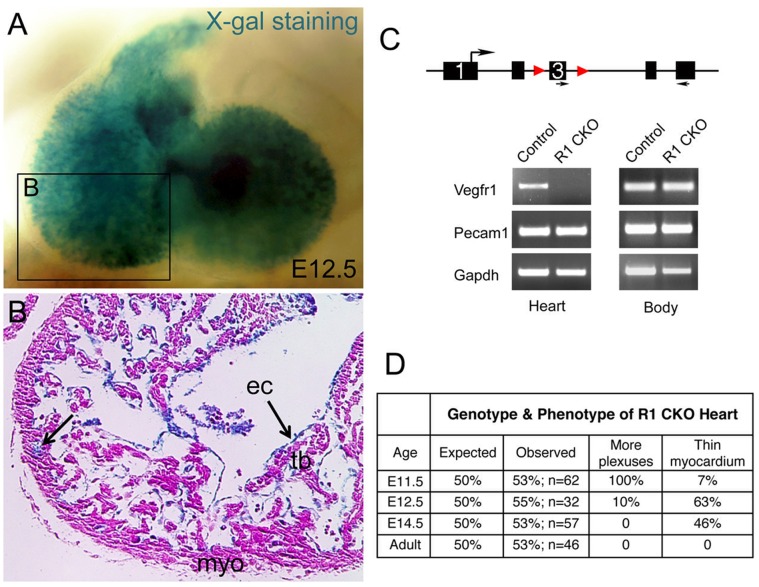
Figure 1. Tissue-specific knockout of Vegfr1 in the endocardium by the Nfatc1Cre line.
A, Wholemount X-gal staining of R26fslz;Nfatc1Cre E12.5 embryo showing the Cre-activated lacZ expression within the heart. B, A frontal sectional view of the cardiac chamber demonstrating lacZ expression in the endocardium (ec; arrows), but not in the compact myocardium (myo) or trabeculae (tb). C, Depicting the endocardial-specific deletion of Vegfr1 in the embryos by the Nfatc1Cre with RT-PCR analysis. D, A table summarizing the phenotypes of R1 CKO heart. An expected frequency (50%) of R1 CKO mice was found at different developmental stages and in adulthood, indicating that endocardial Vegfr1 was not required for survival. However, we observed a complete penetrance of early coronary plexus defect at E11.5, which only remained in a small subset of embryos at E12.5 and was not seen after E14.5. Additionally, half of E12.5 and E14.5 R1 CKO embryos had thin myocardium. The coronary phenotype was determined by immunohistochemistry, whereas the myocardial phenotype was determined by histology.