Figure 1. Changes in cortisol awakening response (CAR) across the experimental groups.
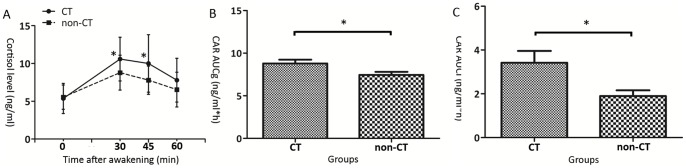
(A) Independent two sample t tests revealed that significant differences of salivary cortisol levels were found between two groups at 30 (t = 2.389, p = 0.021) and 45 min (t = 2.565, p = 0.014) after awakening. Significant increases of cortisol levels were observed in subjects with childhood trauma experiences at those two time points. (B) The CAR area-under-the-curve to ground (AUCg) was significantly differed between two groups (t = 2.335, p = 0.024). Consistent with cortisol levels at 30 and 45 min, subjects who had self-reported childhood trauma showed higher levels of CAR AUCg. (C) With respect to the CAR area-under-the-curve increase (AUCi), significant difference was found as well (t = 2.532, p = 0.016). *Comparison with non-CT group, p <0.05. CT, childhood trauma.
