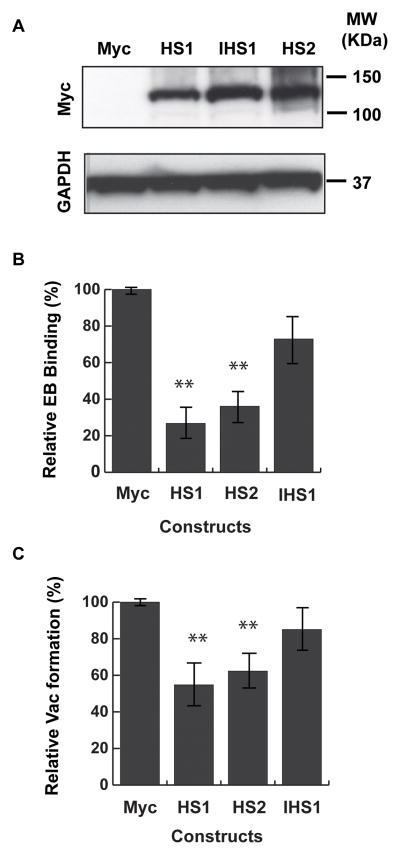
Fig. 1. Overexpression of SULF1 or SULF2 in HeLa cells decreases Chlamydia binding and vacuole formation.
HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the vector expressing Myc-tag alone (Myc) or Myc-tagged SULF1 (HS1), Myc-tagged SULF2 (HS2), or a catalytically inactive version of Myc-tagged SULF1 (IHS1). (A) Levels of Myc-tagged transfected protein were determined by immunoblotting with an antibody to Myc. GAPDH serves as a loading control. (B) For quantitation of EB binding by immunofluorescence microscopy, HeLa cells were transfected for 48 hrs and then infected with C. muridarum for 1 hr. The number of EBs bound per cell was normalized to vector-transfected controls. For vector-transfected controls, the average number of bound EBs/cell was 10.5. Shown is the mean EB binding (± SEM) relative to vector-transfected controls for at least 5 independent experiments. At least 150 cells were counted in each experiment (C) HeLa cells were transfected for 48 hrs and then infected with C. muridarum for 24 hrs. The average number of vacuoles per cell was normalized to vector-transfected controls. For vector-transfected controls, the average number of vacuoles per cell was 0.54. Shown is the mean (± SEM) number of vacuoles per cells normalized to vector-transfected controls for at least 3 experiments. At least 500 cells were counted in each experiment **p < 0.01 ANOVA.