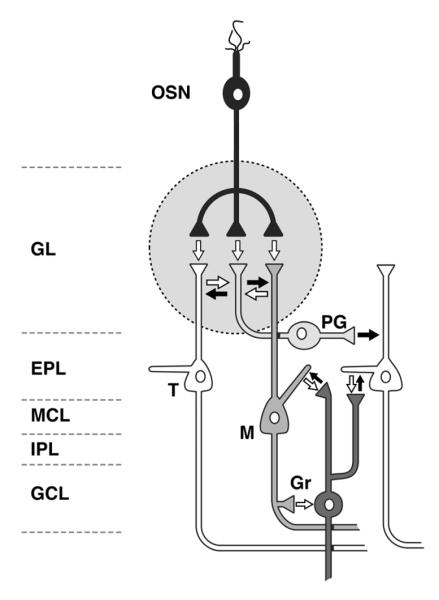
Figure 1.
Circuit diagram of the olfactory bulb and distribution of monoamines. This diagram shows the layers, primary neuronal populations, and synaptic connections of the olfactory bulb (OB). The white arrows represent excitatory connections; the black arrows represent inhibitory connections. Noradrenergic fibers from the locus coeruleus terminate in the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and granule cell layer (GCL), with lower levels of innervation to the external plexiform layer (EPL) and mitral cell layer (MCL). There is very little noradrenergic input to the glomerular layer (GL). Serotonergic fibers from the raphe nucleus project to all layers of the OB: the densest innervation is in the GL, and the MCL, IPL, and GCL are also densely innervated. The EPL is only sparsely innervated by raphe axons. There are no outside dopaminergic projections to the OB. Intrinsic dopaminergic neurons in the OB consist of a subpopulation of neurons within the GL. OSN (olfactory sensory neuron); PG (periglomerular neuron); T (tufted cell); M (mitral cell); Gr (granule cell).