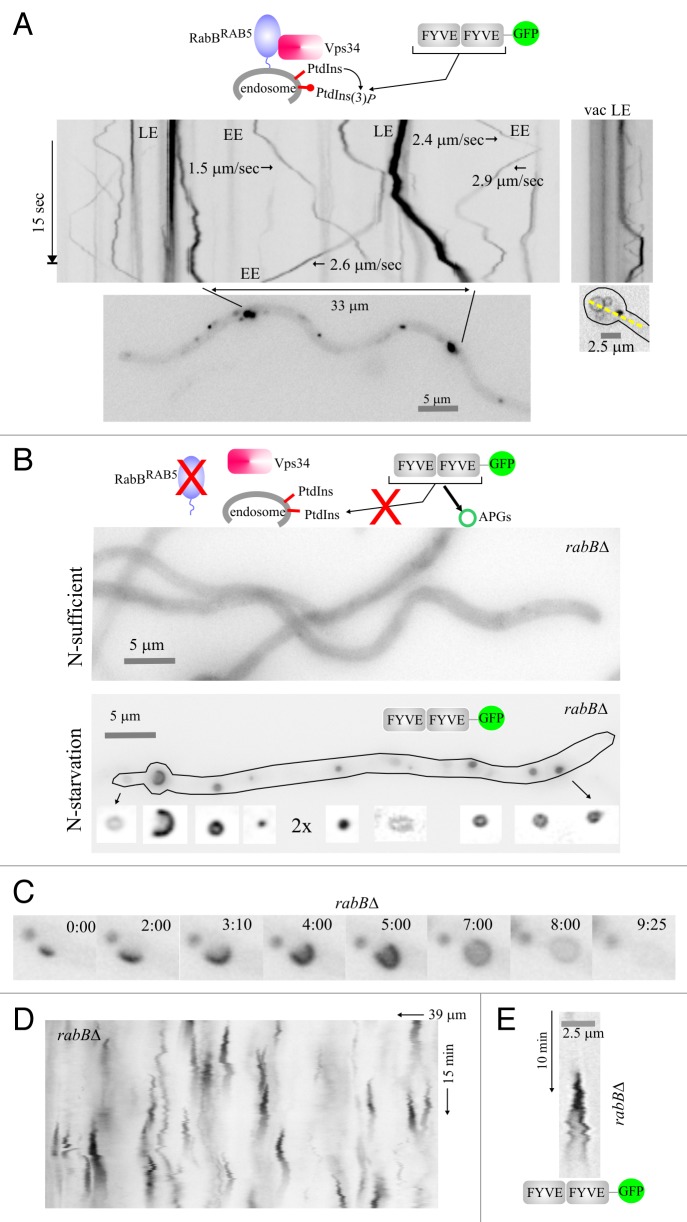
Figure 5. Visualization of PtdIns3P across the autophagosome cycle. (A) In the wild type, cultured in nitrogen-sufficient conditions, RabBRAB5 recruits the Vps34 PtdIns 3-kinase to endosomes. Thus, PtdIns3P-binding FYVE2-GFP localizes to motile endosomes, larger and more static late endosomes and, faintly, to the vacuolar membranes (fluorescence shown in inverted contrast). Stream-acquired time-lapse sequences of the PtdIns3P reporter were used to derive kymographs. The top left image kymograph corresponds to the hyphal region indicated in the bottom image. The rate at which early endosomes move is indicated for some examples. The top right image is a kymograph representation, drawn across the yellow line on the bottom right image, of a basal conidiospore region showing a vacuole and a late endosome. (B) In the rabB∆ mutant, endosomes are depleted of PtdIns3P. Therefore, in nitrogen-sufficient conditions FYVE2-GFP is cytosolic. In contrast, in nitrogen-starved conditions Vps34 synthesizes PtdIns3P on autophagic structures to which FYVE2-GFP is very efficiently recruited. The hypha displayed contains numerous autophagic structures labeled with FYVE2-GFP (shown below the cell at double magnification and improved contrast). (C) Images of a rabB∆ time-lapse sequence showing the different intermediates of an autophagosome cycle, labeled with FYVE2-GFP. Time is in min::sec. (D) Kymograph of a rabB∆ cell expressing FYVE2-GFP, cultured in nitrogen-starved conditions. Fluorescent puncta give rise to cone-shaped figures corresponding to autophagosome cycles. (E) Example of a rabB∆ autophagosome cycle as labeled with FYVE2-GFP. Note that fluorescence gradually declines as the autophagosome enlarges its size.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.