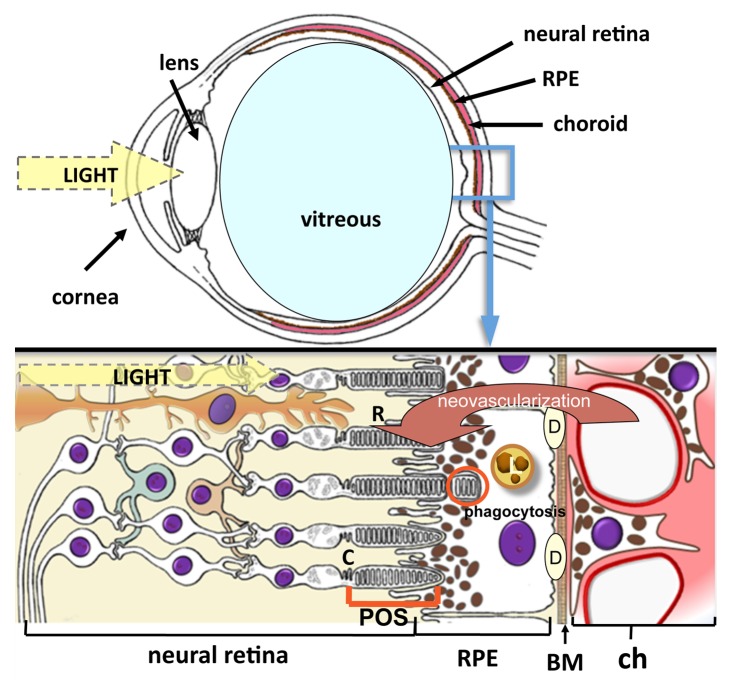
Figure 3. Cross-sectional illustration of the eye and retina. Light reflects via the cornea and lens to the retina. RPE cells have a central role in the pathogenesis of AMD. They absorb light, transport metabolites and nutrients between photoreceptors and the choriocapillaris, produce growth factors, control tissue ionic balance, phagocytose shed tips of photoreceptor outer segments, regulate vitamin A metabolism and visual cycle, and create the blood–retinal barrier. Abbreviations used: R, rods; C, cones; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; POS, photoreceptor outer segments; BM, Bruch’s membrane; L, lipofuscin; D, drusen; ch, choriocapillaris. Red arrow indicates choroidal neovascularization in the wet AMD process.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.