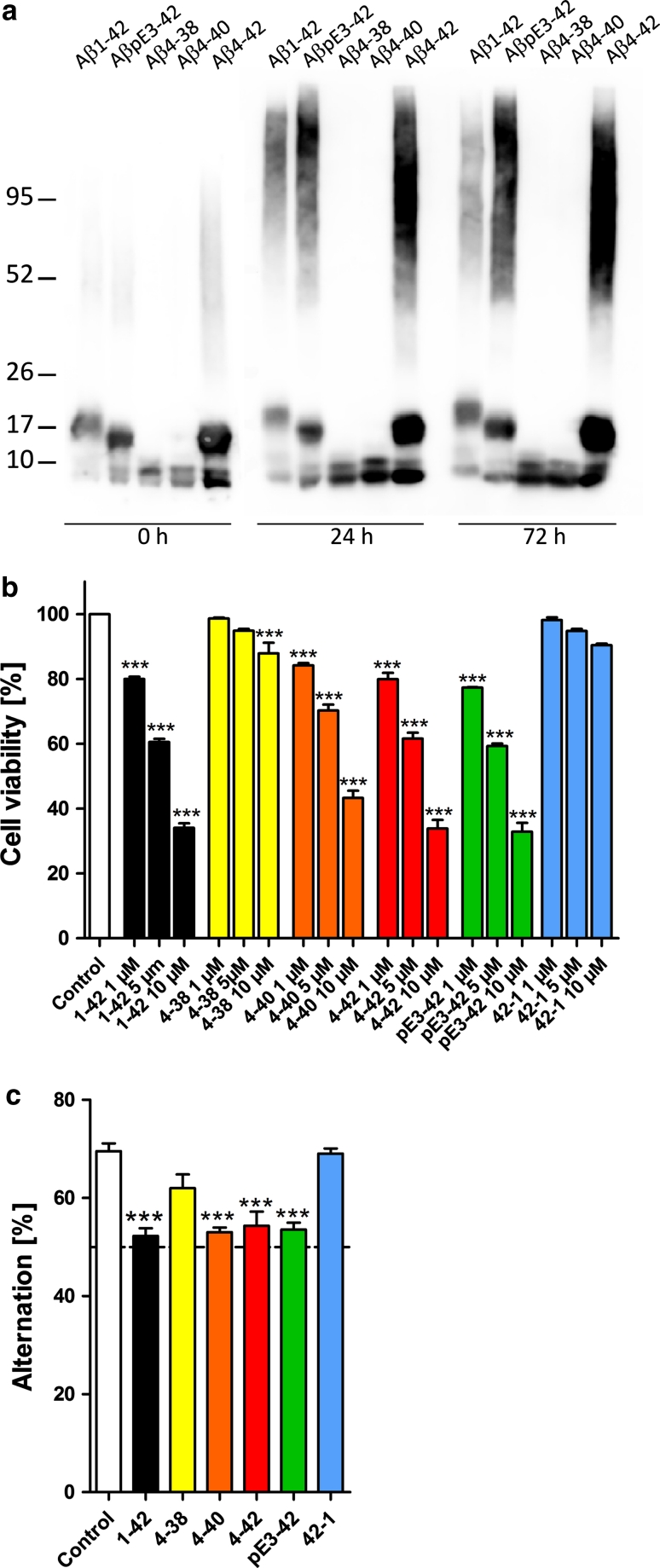
Fig. 3.
Cellular toxicity of N-truncated Aβ peptides. a Freshly prepared Aβ4-38, Aβ4-40,Aβ4-42, AβpE3-42 and Aβ1-42 rapidly formed stable aggregates. All peptides displayed dimeric oligomers and monomers under reducing conditions, while Aβ1-42, AβpE3-42 and Aβ4-42 also developed SDS-stable tri- or tetrameric oligomers. Aged Aβ1-42, AβpE3-42 and Aβ4-42 peptides retained this pattern and exhibited in addition higher molecular weight aggregates. SDS-PAGE Western blot of Aβ peptides using the polyclonal antiserum 24311. b In vitro toxicity with short-term exposure. Primary neurons were treated with Aβ peptides at different concentrations and analyzed by a cell toxicity assay. Aβ1-42 AβpE3-42 and Aβ4-42 demonstrated comparable toxicity profiles followed by Aβ4-40. Aβ4-38 was only toxic at 10 μM. No toxicity was observed with vehicle control and reverse Aβ42-1. c In vivo toxicity of short-term exposure in wildtype mouse brain. Working memory was assessed after intraventricular injection of Aβ4-38, Aβ4-40, Aβ4-42, AβpE3-42 and Aβ1-42 as well as vehicle and reverse peptide control. Mice injected with Aβ4-40, Aβ4-42 AβpE3-42 and Aβ1-42 performed at chance level and showed a significant and robust deficit in working memory. Mice treated with Aβ4-38 demonstrated normal working memory. The same is true for the reverse peptide Aβ42-1 and vehicle control. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons. ***p < 0.001