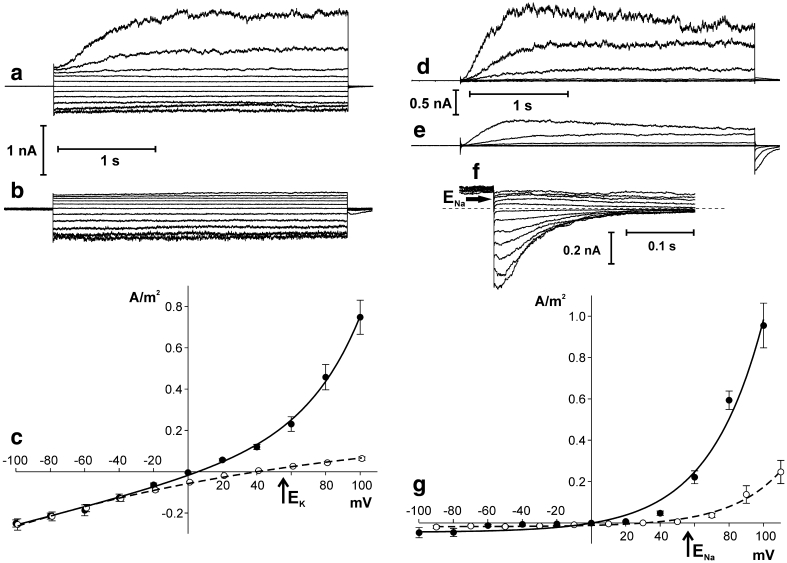
Fig. 1.
Ion channel activity recorded in Physcomitrella patens vacuoles when the current was carried by K+ (a–c) and Na+ (d–g). a Whole-vacuole currents recorded at 100 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM HEPES/Tris, pH 7 in the medium and 100 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM MES/Tris, pH 5.8 in the pipette. b Whole-vacuole currents recorded at 10 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM HEPES/Tris, pH 7 in the medium and 100 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM MES/Tris, pH 5.8 in the pipette. c J–V curves obtained in the same conditions as in a (solid line and closed circles, n = 6) and b (dashed lines and open circles, n = 10), respectively. d Whole-vacuole currents recorded at 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM HEPES/Tris, pH 7 in the medium and 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM MES/Tris, pH 5.8 in the pipette. e Whole-vacuole currents recorded at 10 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM HEPES/Tris, pH 7 in the medium and 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 15 mM MES/Tris, pH 5.8 in the pipette. f Tail currents recorded in the same conditions as in e. Holding voltage (90 mV) lasted 2 s and then test voltages from −30 to 80 mV with 10 mV steps were applied. Dashed line indicates zero current. Horizontal arrow points to the reversal potential. g J–V curves obtained in the same conditions as in d (solid line and closed circles, n = 4) and e (dashed lines and open circles, n = 4), respectively (n denotes different vacuoles). Whole-vacuole recordings were obtained by application of 0.5 s holding voltage (0 mV for a, d, 1 mV for b and 10 mV for e), then 3 s test voltages with 20 mV steps (from 100 to −100 mV for a, d, from 101 to −99 mV for b and from 110 to –90 mV for e), and 0.3 s pulse (0 mV for a, d, 1 mV for b and 10 mV for e) after test voltage