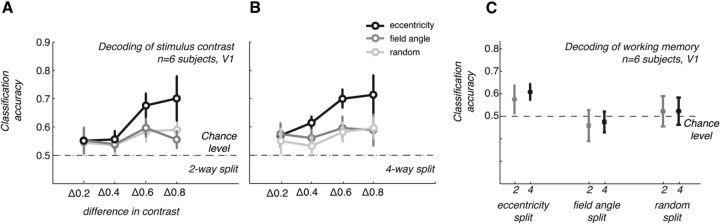
Figure 6.
Robustness of spatial patterns that drive classification (controls). A, B, Classification accuracies by contrast difference in stimuli for the perceived contrast experiment. FMRI responses were averaged in two (A) or four (B) partitions of voxels split according to their eccentricity (black lines, symbols), visual field segment (dark gray), or by random sampling from all voxels in the V1 ROI (light gray). Averaging data into two or four supervoxels within restricted eccentricity bands (dark gray lines) clearly preserves classification accuracies, whereas averaging within visual field (angle) segments or randomly across voxels in V1 does not. C, Classification accuracies for the working memory trials obtained with fMRI responses averaged as in A and B. Symbols indicate the mean across n = 6 subjects. Error bars indicate ± 1 SEM.