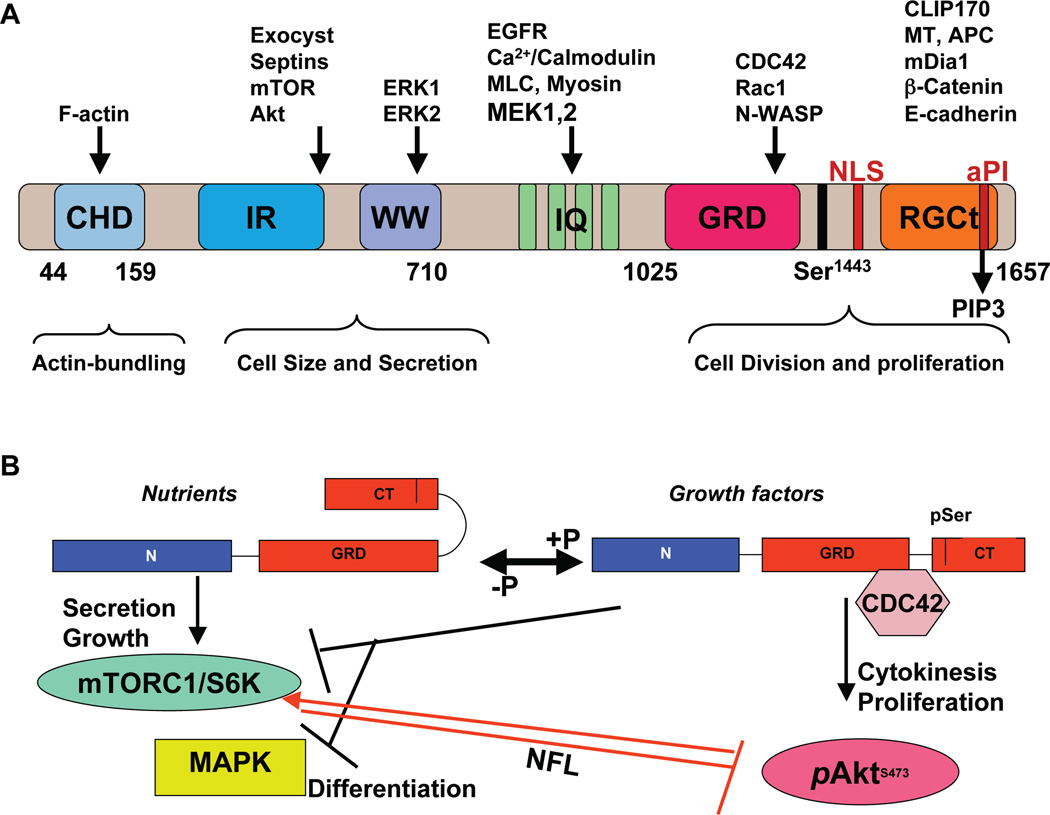
Figure 1. Model of IQGAP1 as a phosphorylation-sensitive molecular rheostat of mTORC-Akt and MAPK signaling controling epithelial homeostasis.
(A) Schematic of IQGAP1 domain structure, relevant binding partners, and cellular functional The amino acids encompassing the domains are indicated beneath the structure. CHD; calponin homology domain; IR-WW: IQGAP1-repeats (IR) and the tryptophan (WW) repeats; IQ: four isoleucine and glutamine rich motifs; GRD: Ras GTPase-activating protein-related domain; RGCT: RasGAP-C terminus (RGCT) domain; the critical Ser-1443 is indicated; NLS: nuclear localization signal; aPI: C2/PH-like domain, which binds PIP3. (B) IQGAP1 modulates mTORC1/S6K1-Akt and MAPK signaling in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. In presence of nutrients, dephosphorylated IQGAP1 has an autoinhibited form by folding of the Cterminal domain, thus masking the Cdc42-binding site to bind mTORC1 and promote secretion and cell growth [Rittmeyer etal., 2008, Wang et al., 2009]. In response to growth factors, phosphorylated pIQGAP1S1443 has an open form that binds Cdc42-GTP and attenuates (black lines) MAPK (Erk1/2) signaling and the mTORC1/S6K negative feedback loop (NFL, red line) inhibition of Akt, thus elevating pAktS473 signal and promoting cell proliferation, while suppressing cell differentiation, and inhibiting secretion [Wang et al., 2009, Tekletsadik et al., 212]. Inability of IQGAP1 to cycle between the two phosphoforms deregulates cell homeostasis leading to transformed phenotypes and neoplasia, if the pathway is tilted to the right, as in cells expressing the phosphomimetic mutant IQGAP1S1443E or cytokinesis arrest and apoptosis, if the pathway is tilted to the left, as in cells expressing IQGAP1IR-WW or the phosphodefective mutant IQGAP1S1443A [Wang et al., 2009, Tekletsadik, et al., 212]