Fig. 6.
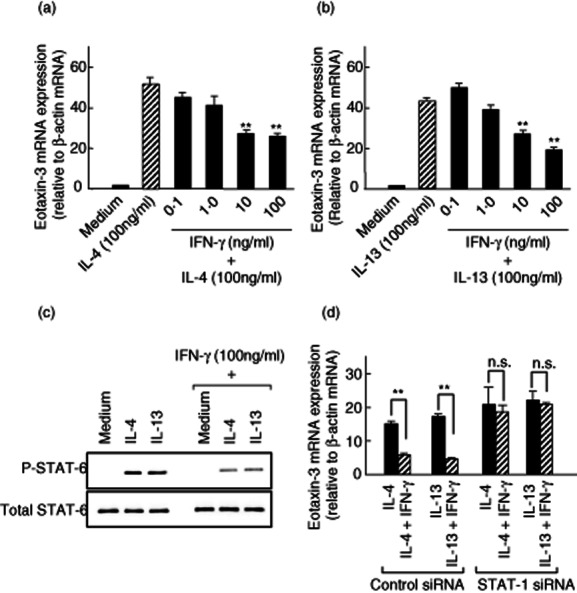
Effects of interferon (IFN)-γ on interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13-induced eotaxin-3 mRNA expression. (a,b) Colonic myofibroblasts, derived from normal mucosa, were stimulated for 24 h with IL-4 (100 ng/ml) or IL-13 (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of increasing concentrations of IFN-γ. Eotaxin-3 mRNA expression was expressed relative to β-actin mRNA expression [mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) from three different experiments]. **P < 0·01 versus IL-4 or IL-13 alone. (c) Effects of IFN-γ on IL-4- and IL13-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription-6 (STAT6) activation. The cells were preincubated with IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) for 3 h, and then stimulated with IL-4 (100 ng/ml) and IL-13 (100 ng/ml) for 15 min. The phosphorylated (p-) and total STAT-6 were detected by Western blotting. (d) Effects of STAT-1 silencing on eotaxin-3 expression. The cells were transfected with the siRNA specific for STAT-1 and incubated for 24 h with IL-4 (100 ng/ml) or IL-13 (100 ng/ml). Eotaxin-3 mRNA expression was expressed relative to β-actin mRNA expression (mean ± s.d. from three different experiments). **P < 0·01.
