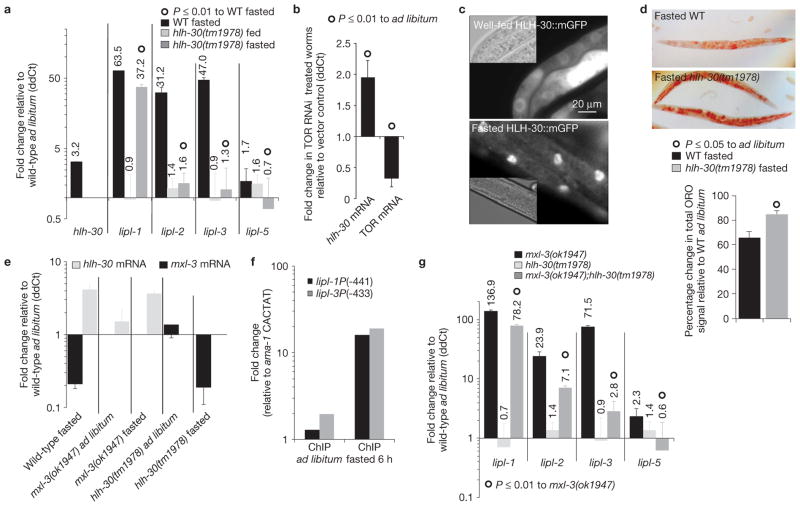
Figure 4.
HLH-30 induces lysosomal lipolysis following fasting. (a) Transcriptional levels of hlh-30 and the mxl-3-dependent lipl genes measured in 5 h fasted wild-type (WT) or hlh-30(tm1978) young-adult worms depicted as mean ddCt + s.e.m. relative to wild-type ad libitum-fed worms show that hlh-30 is induced following fasting and HLH-30 induces lysosomal lipolysis. N = 4 independent experiments for lipl data, n = 2 independent experiments for hlh-30 mRNA. HLH-30 deficiency fully abrogates lipl-2, 3 and 5 (P < 0.0001), and impairs lipl-1 (P < 0.01) transcriptional activation following fasting. (b) Animals treated from late L3 stage with RNAi against TOR or vector control were harvested as young adults. Mean + s.e.m. of three independent experiments shows that inhibition of TOR is sufficient to induce hlh-30 transcription. (c) L3 animals carrying the rescuing construct hlh-30P::HLH-30::mGFP::hlh-30 3′UTR (mGFP, monomeric GFP, and UTR, untranslated region), well fed or fasted for 8 h show that HLH-30 is enriched in intestinal nuclei of fasted worms (exposure time: well fed, 500 ms; fasted, 100 ms). (d) ORO staining of wild-type or hlh-30(tm1978) young adults fasted for 8 h reveals that hlh-30 is required for optimal lipid mobilization on fasting. Mean percentages+s.e.m. are shown below relative to well-fed worms treated in parallel, n = 3 independent experiments. (e) mxl-3 and hlh-30 transcriptional levels in wild-type, hlh-30(tm1978) and mxl-3(ok1947) mutants in the basal and fasted states show that mxl-3 transcription is hlh-30 independent, and hlh-30 transcription is mxl-3 independent. Expression is presented relative to wild-type fed animals as mean ddCt + s.e.m. No significant differences relative to wild type in the same feeding state were observed, n = 3 independent experiments. (f) Representative ChIP-qPCR analysis of well-fed and 6 h fasted mixed stage worms expressing HLH-30::GFP presented as in Fig. 3d shows that HLH-30 occupies the lipl promoters during early fasting. See raw data of two independent experiments in Supplementary Table S9. (g) Transcriptional levels of the mxl-3-dependent lipl genes in wild-type, mxl-3(ok1947), hlh-30(tm1978) or mxl-3(ok1947);hlh-30(tm1978) double mutant young-adult worms show that hlh-30 suppresses the constitutive-induction-of-the-lipl-genes phenotype of mxl-3 mutant animals (mean ddCt + s.e.m. relative to wild-type ad libitum-fed worms). n = 3 independent experiments.