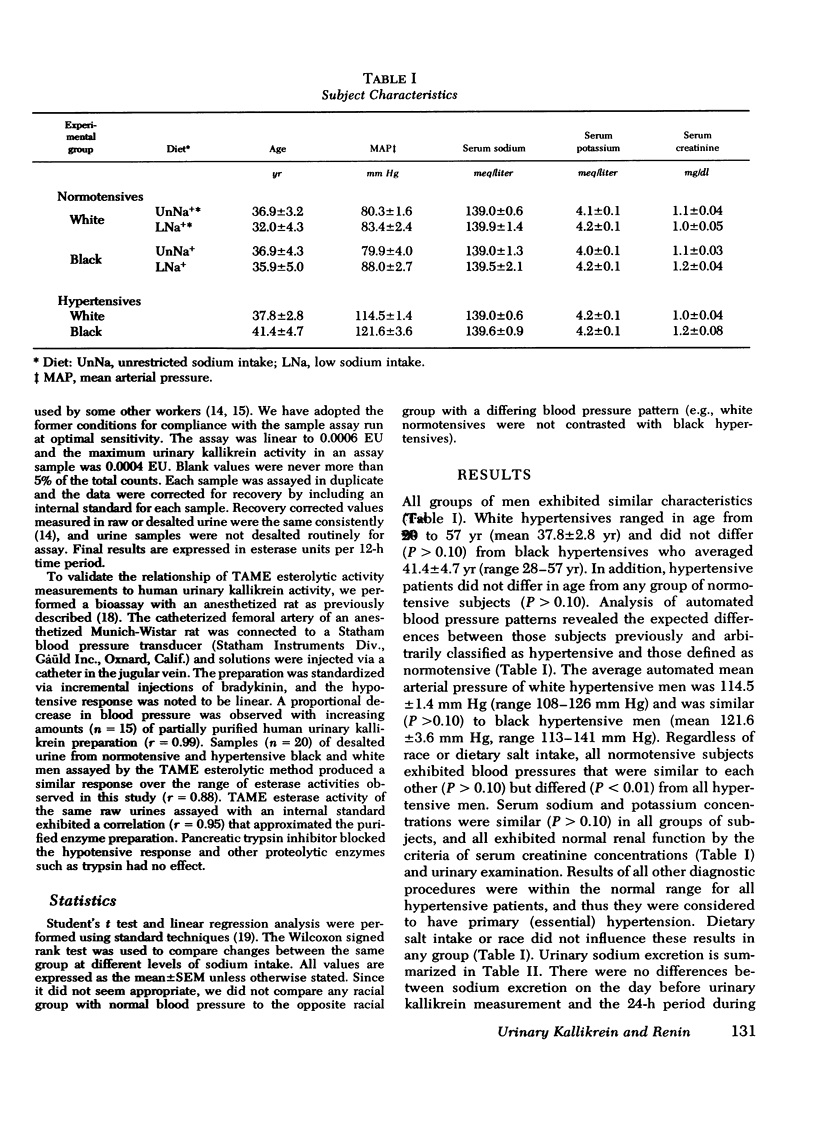
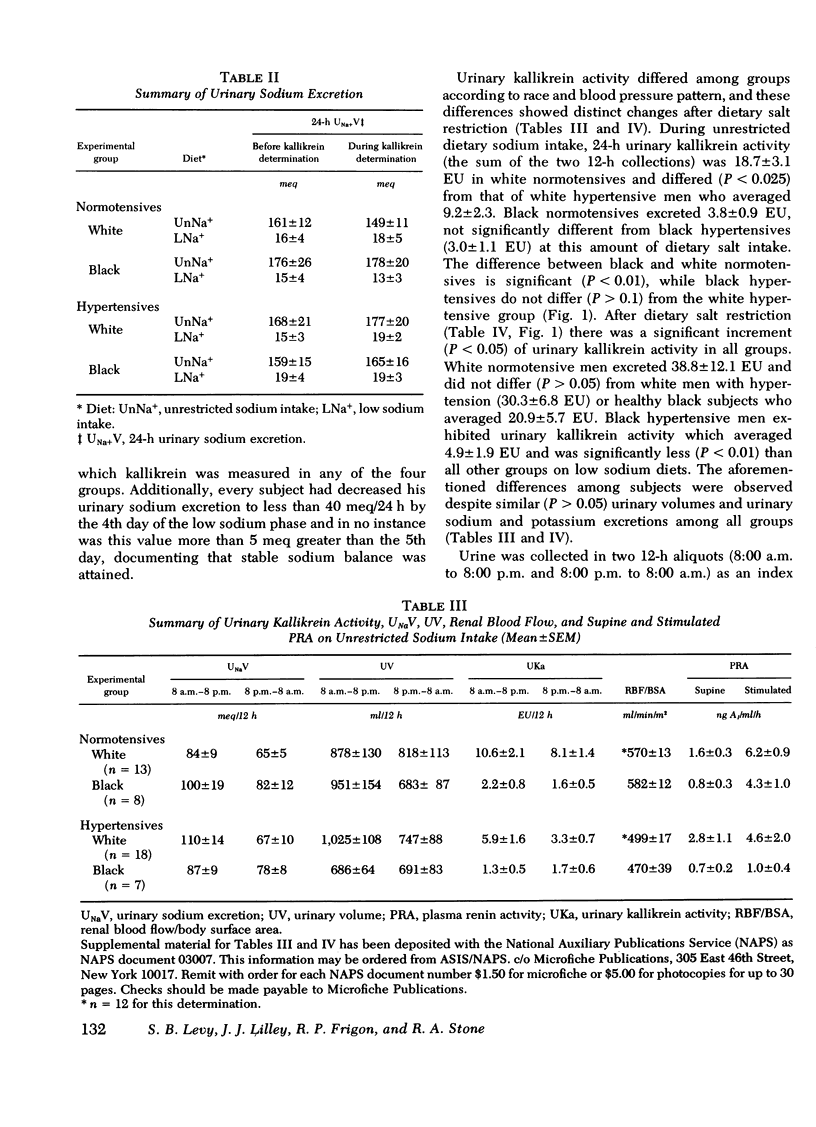
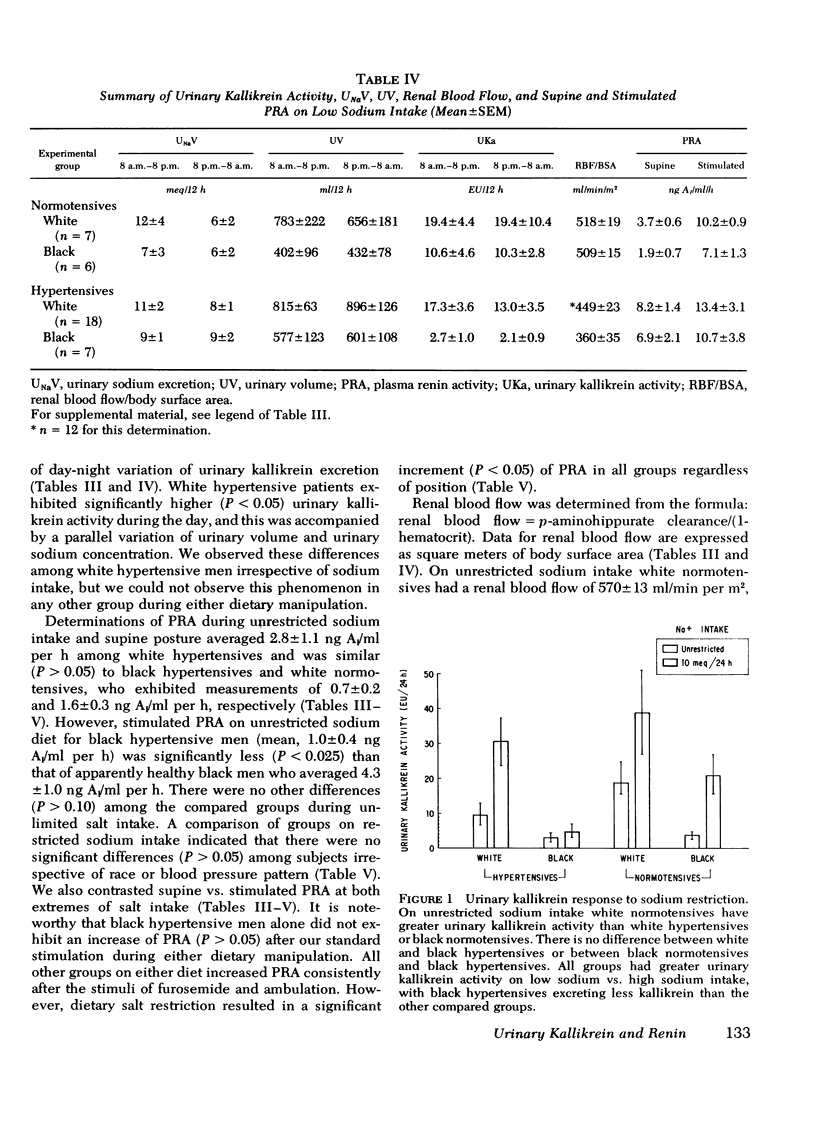
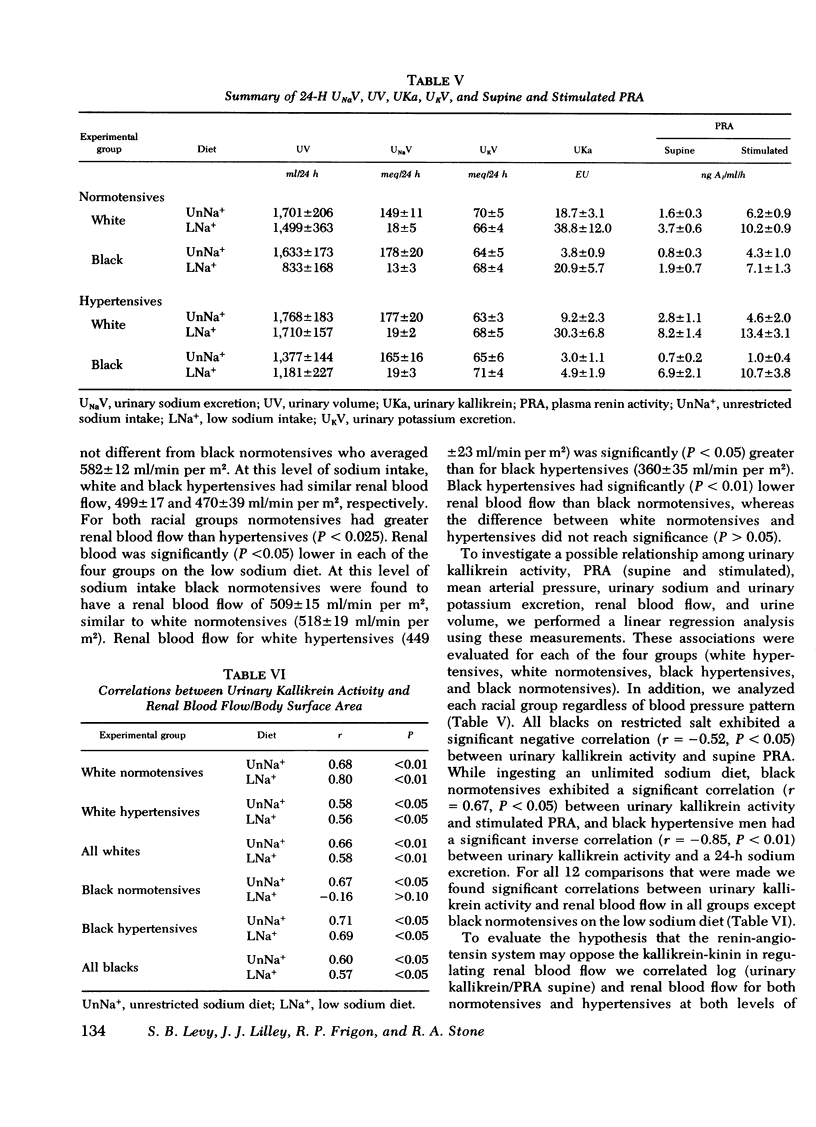
Abstract
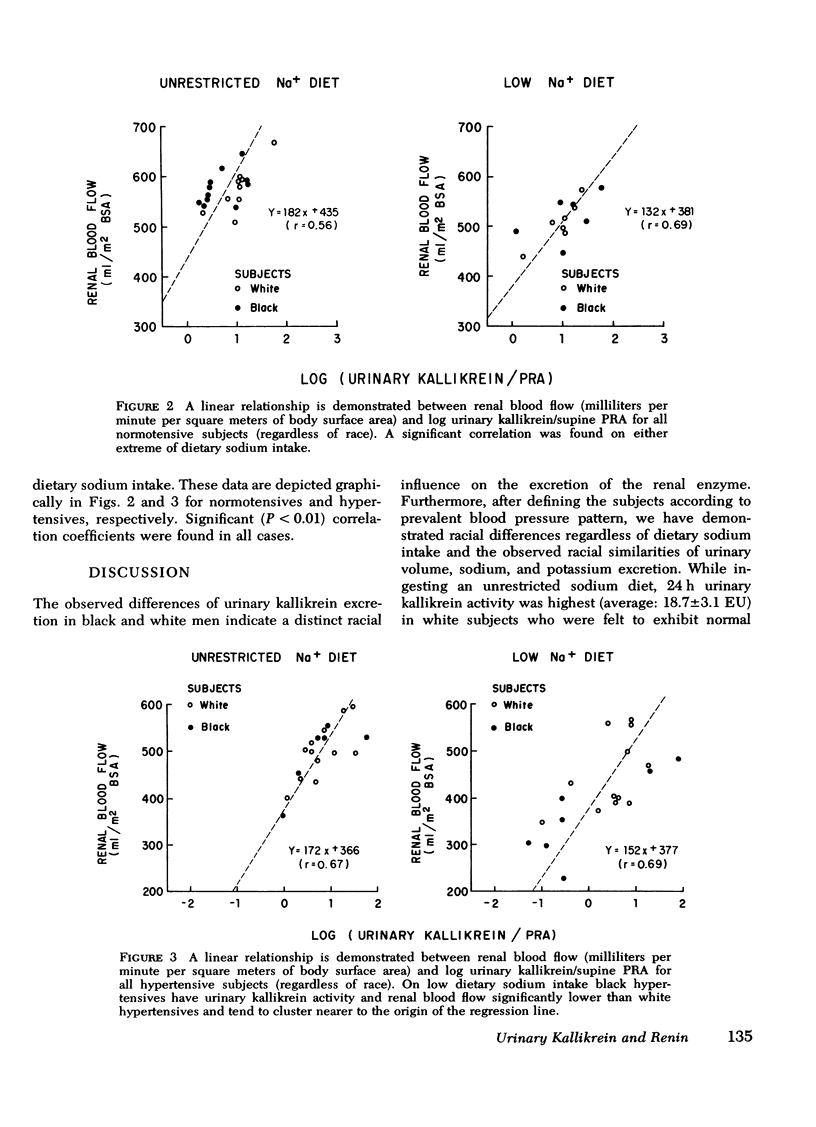
We investigated the relationship of the kallikrein-kinin system and the renin-angiotensin system in the regulation of blood pressure, salt and water excretion, and renal blood flow. Normotensive and hypertensive black and white men were studied during unresticted sodium intake as well as on a 10-meq/day sodium intake; potassium intake was held constant throughout the study (80 meq/day). During unrestricted sodium intake, urinary kallikrein activity was greater in white normotensives than white hypertensives or black normotensives. There was no difference (P greater than 0.05) between white and black hypertensives or between black normotensives and black hypertensives. All groups had greater urinary kallikrein activity on low sodium vs. unrestricted sodium intake, but the increase in black hypertensives was small, and they excreted significantly less kallikrein than the ogher groups on the low sodium diet. Plasma renin activity showed similar increments after sodium restriction in all groups. Urinary kallikrein activity correlated with renal blood flow in all groups except the black normotensives on low sodium intake. Renal blood flow could be correlated uniformly with log (urinary kallikrein activity/supine plasma renin activity) in all groups on either diet. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and urine volume were not different among the groups. We conclude: (a) important racial differences exist in urinary kallikrein activity that are unrelated to sodium or potassium excretion or urine volume; (b) dietary sodium restriction further delineates racial differences and suggests alternative pathophysiologic mechanisms for huma hypertension; (c) urinary kallikrein activity correlates with renal blood flow; and (d) our data support the concept that the kallikrein-kinin system and the renin-angiotensin system contribute to the regulation of renal blood flow and may account for racial differences in renal vascular resistance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adetuyibi A., Mills I. H. Relation between urinary kallikrein and renal function, hypertension, and excretion of sodium and water in man. Lancet. 1972 Jul 29;2(7770):203–207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayless T. M., Rosensweig N. S. A racial difference in incidence of lactase deficiency. A survey of milk intolerance and lactase deficiency in healthy adult males. JAMA. 1966 Sep 19;197(12):968–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven V. H., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. A sensitive isotopic procedure for the assay of esterase activity: measurement of human urinary kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Oza N. B., Scigli A. G., Schork A. Renal tissue kallikrein, plasma renin and plasma aldosterone in renal hypertension. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1974;24(5):448–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. Renal kallikrein: its localization and possible role in renal function. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. S., Erdös E. G., Miwa I., Tague L. L., Coalson J. J. Isolation from a salivary gland of granules containing renin and kallikrein. Circ Res. 1968 Oct;23(4):507–517. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. R., Giangiacomo J., Ingelfinger J. R., Robson A. M. Measurement of renal function without urine collection. A critical evaluation of the constant-infusion technic for determination of inulin and para-aminohippurate. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 30;287(22):1109–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211302872202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Formation of human plasma kinin. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 5;291(10):509–515. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409052911008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Tague L. L., Miwa I. Kallikrein in granules of the submaxillary gland. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 May;17(5):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton A. C., Coleman T. G., Cowley A. V., Jr, Scheel K. W., Manning R. D., Jr, Norman R. A., Jr Arterial pressure regulation. Overriding dominance of the kidneys in long-term regulation and in hypertension. Am J Med. 1972 May;52(5):584–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Diniz C. R., Mares-Guia M. Purification and properties of a human urinary kallikrein (kininogenase). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4311–4318. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. S., Delvin D. G. Ineffectiveness of propranolol in hypertensive Jamaicans. Br Med J. 1968 Jun 8;2(5605):601–603. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5605.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. R., Geller R. G., Margolius H. S., Pisano J. J. Urinary kallikrein in hypertensive animal models. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley J. J., Hsu L., Stone R. A. Letter: Racial disparity of plasma volume in hypertensive man. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jun;84(6):707–708. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-6-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS P. A., GROSS R. T. Erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: evidence of differences between Negroes and Caucasians with respect to this genetically determined trait. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2253–2262. doi: 10.1172/JCI104006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald J. M., Webster M. M., Jr, Tennyson C. H., Drapanas T. Serotonin and bradykinin in the dumping syndrome. Am J Surg. 1969 Feb;117(2):204–213. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Geller R., Pisano J. J., Sjoerdsma A. Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet. 1971 Nov 13;2(7733):1063–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Geller R. G., De Jong W., Pisano J. J., Sjoerdsma A. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertension. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Geller R. G., Alexander R. W., Gill J. R., Jr, Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in normal man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):812–819. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertensive man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):820–825. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Colina-Chourio J. Interaction of mineralocorticoids, renal prostaglandins and the renal kallikrein-kinin system. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):189–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K., Rubin I. Subcellular localization of renin and kininogenase in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):326–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K. The relationship between kidney and urinary kininogenase. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 May;39(1):73–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli G., Bianchi G., Croxatto H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in a spontaneously hypertensive strain of rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Sep;149(4):983–986. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS P. S. Measurement of the rate of plasmin action on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman H., Silverberg E., Holleb A. I. Cancer statistics, 1976 a comparison of white and black populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 1976 Jan-Feb;26(1):2–30. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.26.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Congbalay R. C., Karsh D. L., Osgood R. W., Ferris T. F. The effect of bradykinin on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption in the dog: evidence for functional nephron heterogeneity. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1709–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI106972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeten D. H., Kerr C. B., Kerr L. P., Prior J. C., Dalakos T. G. Hyperbradykininism: a new orthostatic syndrome. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1048–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach L., Nyarai I., Dawson K. G. Stimulated renin: a screening test for hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jan;82(1):27–34. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Tuck M. L., Rose L. I., Dluhy R. G., Underwood R. H. Studies of the control of plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man. 3. Response to sodium chloride infusion. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2645–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI107082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Talamo R. C., Williams G. H., Colman R. W. Response of the kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems to saline infusion and upright posture. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):691–698. doi: 10.1172/JCI107978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


