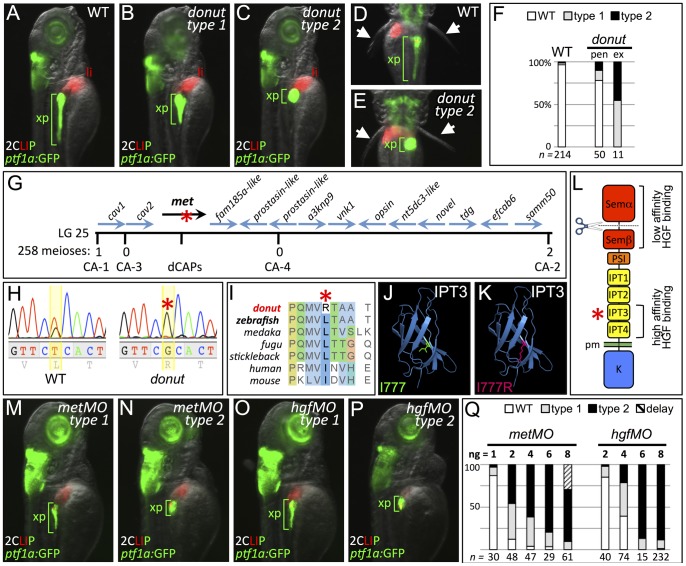
Figure 1. donuts908 is a hypomorphic allele of met.
(A–E) Exocrine pancreas (xp) structure marked by ptf1a:GFP expression in 3 dpf WT (A,D), and in type 1 (B) and type 2 (C,E) donut mutants. The pectoral fins (arrowheads) of donut mutants lack muscle tone, often asymmetrically, leading to their “open wing” appearance (right arrow, E). (F) Penetrance (pen) and expressivity (ex) of the donut phenotype. A small fraction of WT embryos shows donut-like pancreatic phenotypes, while 22% of clutchmates from heterozygous intercrosses exhibited either a spherical (55%) or an intermediately shortened (45%) pancreas. n below bars represents the number of embryos examined from WT clutches (right), heterozygote in-crossed clutches (center), and embryos exhibiting donut-like pancreatic phenotypes (right). (G–I) donut mutants have a lesion in met. donut was mapped to a critical interval on Chr. 25 containing 14 annotated genes (G); met showed a T2324G variant (H) causing an L775R amino acid substitution (I). (J,K) Model structures of the human MET IPT3 domain with isoleucine 777 (analogous to zebrafish residue L775) marked green (J) or substituted arginine marked red (K). (L) Diagram of Met showing the I777R substitution localized to the high affinity HGF binding site in IPT3, and the furin cleavage site in the semaphorin-like domain. (M–P) Morpholino-mediated knockdown of met (M,N) or hgfa/b (O,P) resulted in phenocopy of the donut mutation. (Q) Dose dependence of morpholino-induced phenotypes. At 8 ng, metMO exhibited some non-specific developmental delay, suggesting toxicity. pen, penetrance; ex, expressivity; li, liver; pm, plasma membrane.