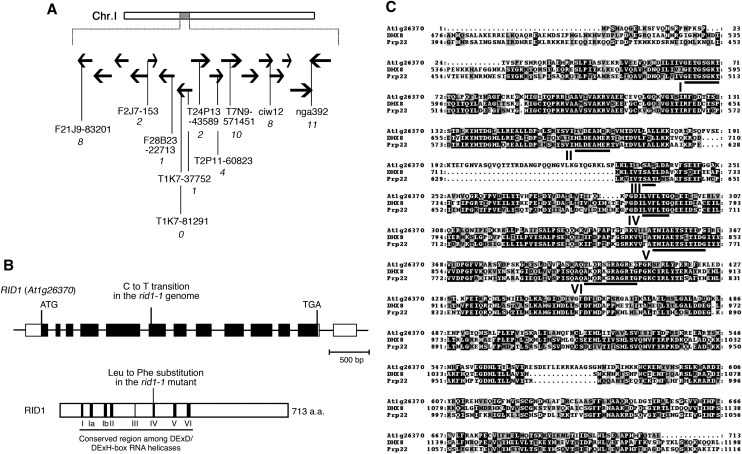
Figure 4.
Chromosome Mapping of the RID1 Locus and Alignment of Amino Acid Sequences.
(A) Chromosomal location of the rid1-1 mutation. Black horizontal arrows represent BAC clones around the RID1 locus on chromosome I. The number of recombination events between DNA polymorphism markers and the RID1 locus is given in italicized numerals beneath the marker names.
(B) Structure of RID1 (top) and its encoded protein (bottom). Black boxes represent exons, lines represent introns, and unfilled boxes represent 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions (top). The position of the single-base substitution in rid1-1 is indicated. The highly conserved DEAH-box RNA helicase region is underlined, and motifs I to VI are numbered (bottom). a.a., amino acids.
(C) Alignment of amino acid sequences of RID1, human DHX8, and yeast Prp22. Alignment was generated with the ClustalW program. Identical residues are highlighted on a black background, and similar residues are shaded in gray. The highly conserved DEAH-box RNA helicase domains are underlined and labeled motifs I to VI.