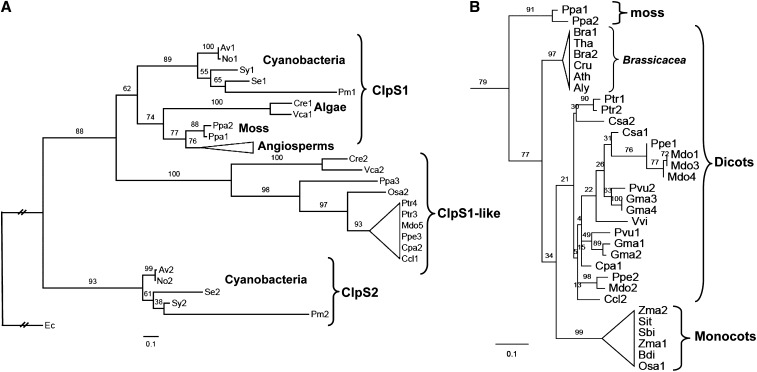
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic Analysis of ClpS.
(A) Schematic Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood (RAxML) phylogeny of 57 ClpS proteins from E. coli, five cyanobacterial species, twp algal species, moss, and 19 angiosperms. RAxML bootstrap support values are shown at the nodes of the tree, in which the E. coli ClpS is designated as the outgroup and ClpS relatives are classified into six clades: ClpS1 proteins from cyanobacteria, algae, moss, and angiosperms, ClpS2 protein from cyanobacteria, and ClpS1-like protein. ClpS1 and ClpS1-like proteins (39 in total) in angiosperms are collapsed and indicated as a triangle. Details for this angiosperm clade are shown in (B). The complete sequence alignment is shown in Supplemental Figure 1 online (excluding the cTPs) and is available as Supplemental Data Set 1 online. The species included are Physcomitrella patens (Ppa), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cre), Volvox carteri (Vca), Anabaena variabilis ATCC 29413 (Av), Nostoc sp PCC 7120 (No), Synechocystis sp PCC 6803 (Sy), Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (Se), Prochlorococcus marinus subsp marinus str. CCMP1375 (Pm), Escherichia coli str. K12 substr. W3110 (Ec). The 19 angiosperm species included are the 14 dicotyledons Populus trichocarpa (Ptr), Phaseolus vulgaris (Pvu), Glycine max (Gma), Cucumis sativus (Csa), Prunus persica (Ppe), Malus domestica (Mdo), Arabidopsis thaliana (Ath), Arabidopsis lyrata (Aly), Capsella rubella (Cru), Brassica rapa (Bra), Thellungiella halophila (Tha), Carica papaya (Cpa), Citrus clementina (Ccl), Vitis vinifera (Vvi), and the five monocotyledons Sorghum bicolor (Sbi), Zea mays (Zma), Setaria italica (Sit), Oryza sativa (Osa), and Brachypodium distachyon (Bdi). Distance is indicated as substitutions per site.
(B) Phylogeny of the ClpS1 clade for the angiosperms and moss. ClpS1 proteins in Brassicaceae are separated in a single clade distinct from the others, including those in monocots. Distance is indicated as substitution rate per site.