Figure 11.
Identification of Candidate ClpS1 Substrates by Affinity Chromatography.
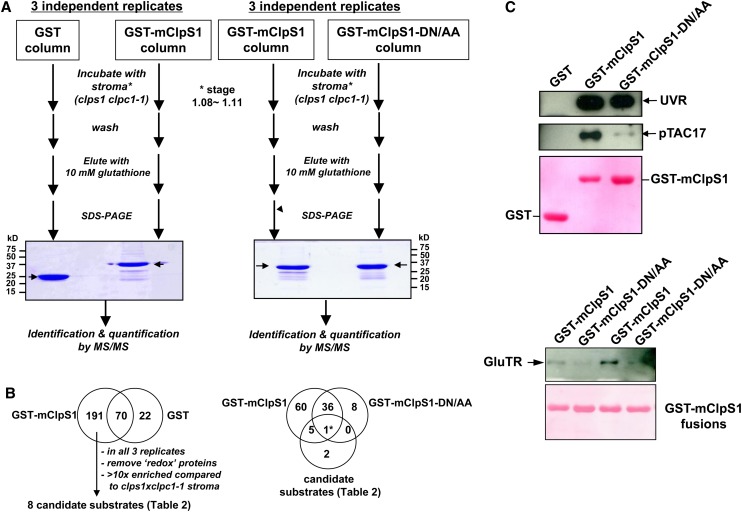
(A) The workflow for the ClpS1 affinity purification and subsequent MS-based protein identification of ClpS1 substrate candidates. Representative gel images of pull-down eluates using wild-type and mutant (DN/AA) versions of GST-ClpS1 fusions, or the negative control GST, as bait proteins. The arrow indicates eluted GST or GST-ClpS1 (bait). Some of the visible bands represent breakdown products of recombinant GST or GST-ClpS1.
(B) The workflow used to choose candidate ClpS1 substrates. The Venn diagram on the left shows those proteins identified using either GST or GST-ClpS1 as bait. From the 191 proteins only identified in the GST-ClpS1 affinity experiments, we considered only those candidate substrates that were observed in all three independent replicates that were also at least 10-fold enriched compared with the stroma of clps1 clpc1-1. Moreover, proteins with glutathione binding domains or thioredoxins were removed. The resulting eight candidate substrates were then compared with the proteins identified in a separate set of GST-ClpS1 and GST-ClpS1-DN/AA affinity assays as indicated in the Venn diagram on the right. Details of the candidate substrate proteins can be found in Table 2.
(C) Confirmation of ClpS1 interactions by immunoblotting. Eluates were transferred to blots and probed with antisera raised against pTAC17, the UVR protein, or GluTR. Ponceau stains of the blots are shown and visualize the recombinant bait.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]