Figure 5.
Analysis of a ClpS1 Null Mutant in Arabidopsis.
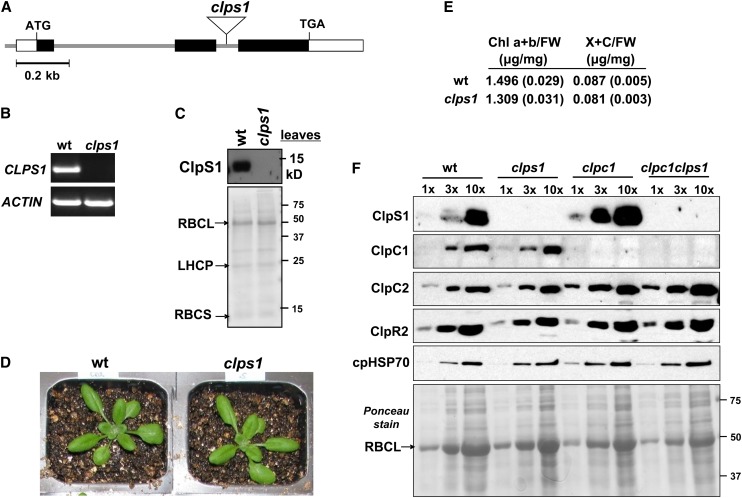
(A) Gene model structure and position of T-DNA insertion in the CLPS1 null mutant used in this study. Exons (black boxes for coding sequence), 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (open boxes), and T-DNA insertion (triangle) are indicated.
(B) CLPS1 transcript accumulation in the wild type and clps1. Transcripts were extracted from wild-type and clps1 seedlings and amplified by RT-PCR with gene-specific primers and analyzed on an agarose gel. ACTIN mRNA was used as an internal control.
(C) To determine if ClpS1 was absent in clps1, total leaf protein extracts from the wild type and clps1 were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The filter was also stained with Ponceau S (bottom panel).
(D) Comparison of wild-type (wt) and clps1 phenotypes. Plants were grown for 20 d on soil under 16/8-h light/dark cycle at ∼120 µmol photons m−2 s−1. No visible differences were observed.
(E) Pigment accumulation in soil-grown wild-type and clps1 seedlings at developmental stage 1.07. Plants were grown under a 10-h-light/14-h-dark period at ∼100 μmol photons m−1 s−2. Chlorophyll a+b (Chl a+b) and total xanthophyll and other carotenoid (X+C) contents were determined on a fresh weight basis; n = 6. se is indicated.
(F) Upregulation of ClpS1 and ClpC2 proteins in the clpc1-1 mutant background. Stromal proteins were isolated from wild-type, clps1, clpc1-1, and clps1 clpc1-1 seedlings and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ClpS1, ClpC1, ClpC2, ClpR2, and cpHSP70 antibodies. A titration of proteins was loaded for each genotype, as indicated. The filter was stained with Ponceau S (bottom panel).
[See online article for color version of this figure.]