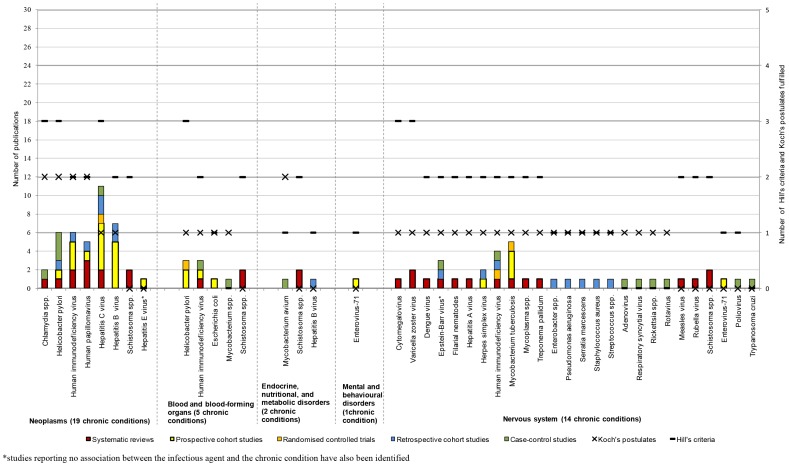
Figure 5. Number of publications per study type for neoplasms, blood and blood-forming organs, endocrine, nutritional and metabolic disorders, and nervious system (year 2001–2010).
The chronic conditions were grouped into disease areas according to the highest hierarchy level in the International System for Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10. Associations between infectious agents and chronic conditions belonging to 15 disease areas were identified (Figures 5, 6, 7, 8). The numbers of publications per infectious agent were quantified and, for each infectious agent, the publications were presented according to study type (i.e., systematic reviews, prospective cohort studies and RCTs, retrospective cohort studies, and case-control studies). For each infectious agent and disease area, the total numbers of Hill's criteria and Koch's postulates fulfilled were determined. In the figures, the infectious agents were ranked, first according to the number of Koch's postulates fulfilled and secondly according to the number of Hill's criteria fulfilled. In this dataset, the strongest associations were those between chronic conditions of the circulatory system and C. pneumoniae or T. cruzi, and between chronic conditions of the genitourinary tract and C. trachomatis.