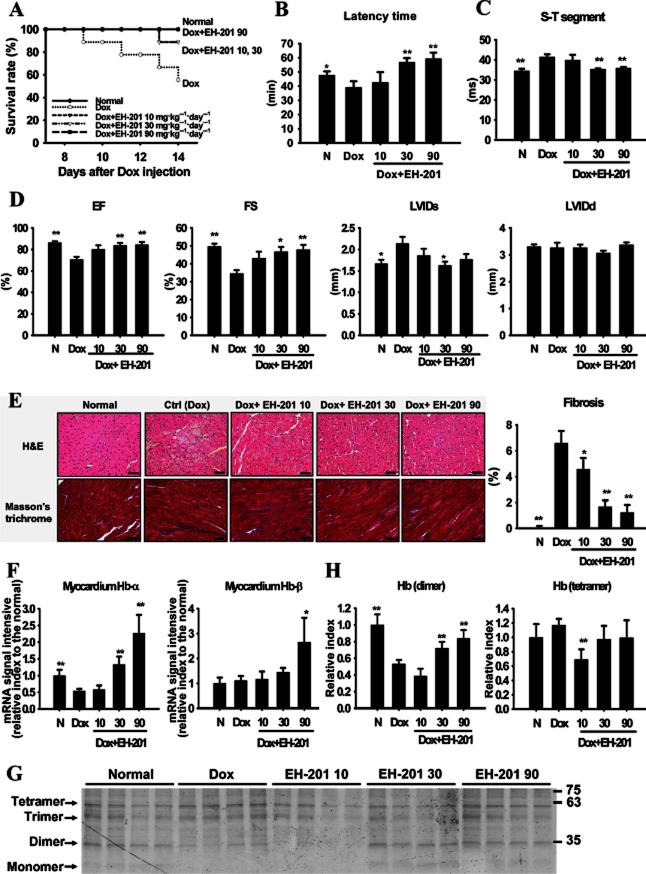
Figure 5.
EH-201 has therapeutic effects on cardiac dysfunction in doxorubicin (Dox)-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. (A) The survival rate was analysed using the Kaplan–Meier method (detailed treatment protocol in Methods). The normal (N) group represents saline injection. (B) The effect of EH-201 treatment on mice performing the hypoxic rotarod endurance test 2 weeks after Dox injection. (C, D) The effect of EH-201 on cardiac abnormality and functionality was characterized by ECG and echocardiography. EF, ejection fraction; FS, fractional shortening; LVIDs/d, left ventricular internal diameter at systole/diastole. (E) Representative photomicrographs of left ventricular sections of mouse hearts stained with haematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichrome (left, bars = 10 μm). The blue staining indicates fibrosis, and quantification of the interstitial fibrosis was performed (right). (F) Isolated myocardium tissues after 2 weeks of Dox were analysed for Hb expression by Q-PCR and (G) a TMBZ stain of each myocardium lysate of the treatment groups in SDS-PAGE was performed, with (H) quantitative values. The values are presented as the means ± SEM (n = 5–6 animals each group). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 versus Dox group by one-way anova with Tukey's post hoc test.