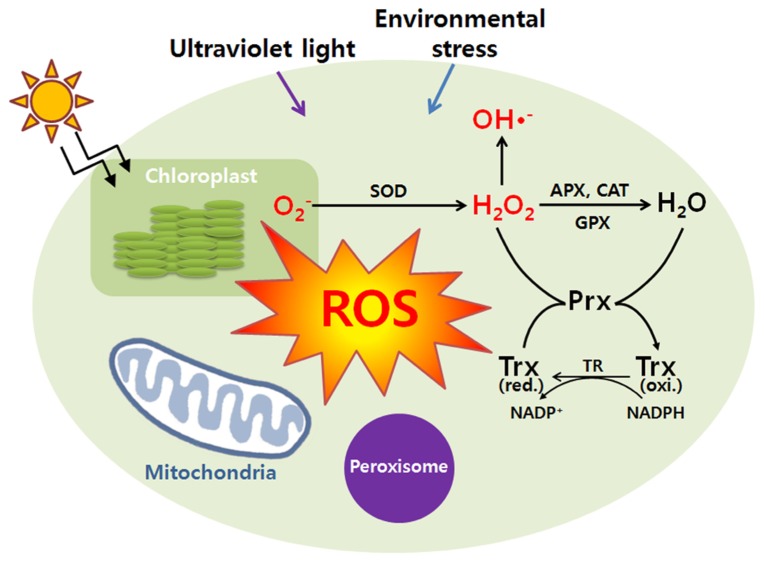
FIGURE 1.
Cellular responses against reactive oxygen species. During a variety of stress conditions (UV, environmental stress, etc), reactive oxygen species (ROS) can be generated. At the start of the reaction, a primary ROS which is superoxide anion (O2-) can be formed by the one electron reduction of molecular oxygen. The superoxide anion (O2-) is dismutated by superoxide dismutase (SOD) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) which is detoxified by catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and peroxiredoxin (Prx). Once the superoxide anion (O2-) is formed in the presence of H2O2, it becomes inevitable. Further reactions may lead to the formation of hydroxyl radicals (HO·). Antioxidant proteins protected the damages of ROS leaking from peroxisomes. H2O2 can easily permeate the peroxisomal membrane and play an important role in protection of cells from ROS damages. And various ROS transmitted to the mitochondrion play a role in the adaptive response of mitochondrial redox state, especially for the reduction state of respiratory pathways. The redox signals will be transmitted to the nucleus to regulate plant growth and developments. Trx represents thioredoxin.