Fig. 9.
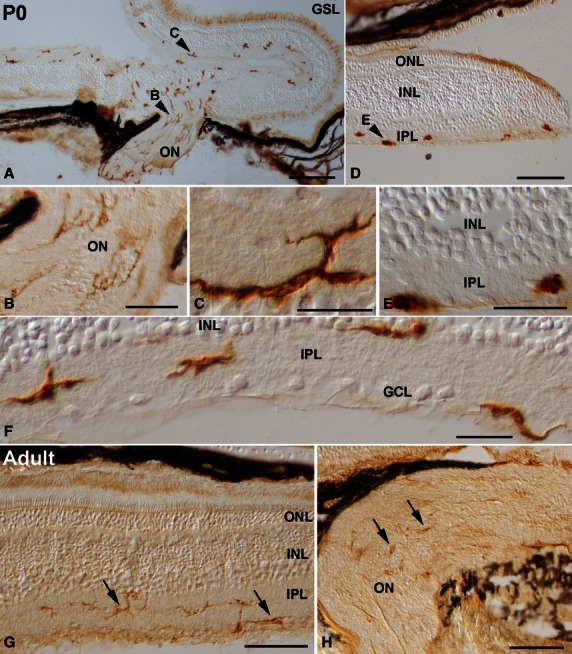
Spatial pattern of lectin-positive cells in the P0 (A-F) and adult (G,H) retina of the small-spotted catshark. Cryosections from retinas were treated according to the GSL histochemistry technique. Arrowheads in (A,D) point to cells shown at higher magnification in (B,C,E). Abundant ramified lectin-positive cells that extended thin processes coursing parallel to the ganglion cell axons were detectable in the optic nerve (A,B). Many ramified labelled cells were also distinguishable in the IPL of the central retina (A,C,F). Lectin-positive cells in the peripheral regions of the retina were round and amoeboid in shape (D,E). At P0, most of the labelled cells were oriented parallel to the vitreal surface, and showed a stratification pattern within the IPL: they were located in the border between the IPL and the INL, in the border between the IPL and the GCL, and in the middle of the IPL (F). In the adult shark visual system, the intensity of lectin labelling diminished (arrows in G,H). Lectin-positive cells showed a well ramified shape, with most of their processes oriented parallel to the vitreal surface of the retina (arrows in G). Note that labelled cells were mainly located in the IPL (arrows in G). Lectin-positive cells in the optic nerve revealed a weak histochemical signal (arrows in H). GCL, ganglion cell layer; GSL, Griffonia simplicifolia lectin; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ON, optic nerve; ONL, outer nuclear layer. Scale bars: 200 μm (A,D); 50 μm (B); 20 μm (C,E,F); 100 μm (G,H).
