Figure 4. Edited Octopus Potassium Channels Close More Quickly.
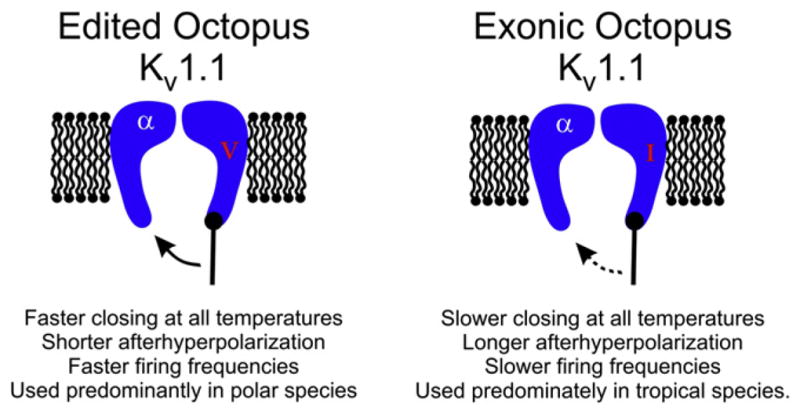
Editing of octopus Kv1.1 at position I321V in the fifth transmembrane span destabilizes the open state, allowing the channels to close rapidly upon repolarization. The overall physiological effect would be to reduce the length of the afterhyperpolarization, allowing higher firing frequencies. Because this site is highly edited in polar species and scarcely edited in tropical species, it is hypothesized to be an adaptation to temperature. The dashed arrow indicates a slower rate.
