Figure 2. Adipocyte XBP1 deletion disturbs metabolic flux during lactation.
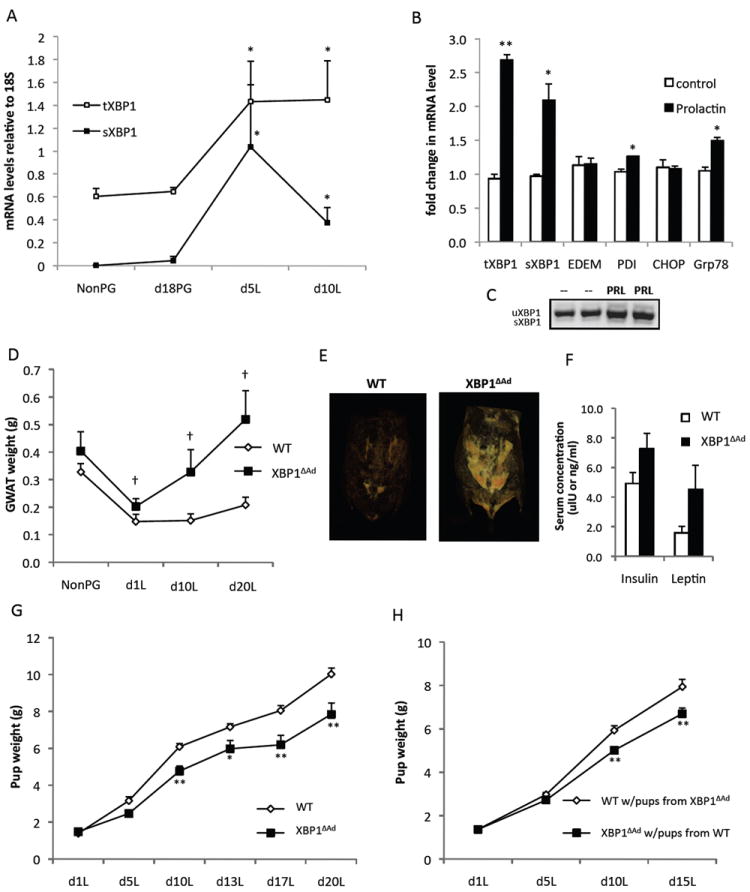
(A) mRNA levels of Xbp1 in gonadal adipose tissue from WT mice that were non-pregnant (NonPG), in late pregnancy (d18PG), or in day 5 or 10 of lactation(L). (B) Fully differentiated adipocytes were treated with or without prolactin for 6 hours and mRNA levels of UPR genes were measured by QPCR. (C) Both spliced and unspliced forms of XBP1 are shown. (D) Gonadal white adipose tissue (GWAT) wet weights of WT and XBP1ΔAd dams from non-pregnant (NonPG) and day 1, 10 and 20 lactation (L) timepoints (n=4-9). (E) Representative images from CT scans of WT and XBP1ΔAd dams during peak lactation (day 12). Adipose tissue density is displayed. (F) Serum insulin and leptin levels of WT and XBP1ΔAd dams at day 20 lactation (n=3). (G) Pup weights of litters nursed by WT or XBP1ΔAd dams during lactation. All litters are mixtures of pup genotypes (WT and XBP1ΔAd) (n=6-10 litters per genotype). (H) Cross-foster of XBP1ΔAd and WT litters. Average pup weight during lactation from cross-fostered litters switched on day 1 lactation (n=8-10, litters were pared to 6 pups). All error bars indicate +/- SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 using standard t-test. † denotes p<0.007 as measured by regular 2-way ANOVA. See also Figure S2.
