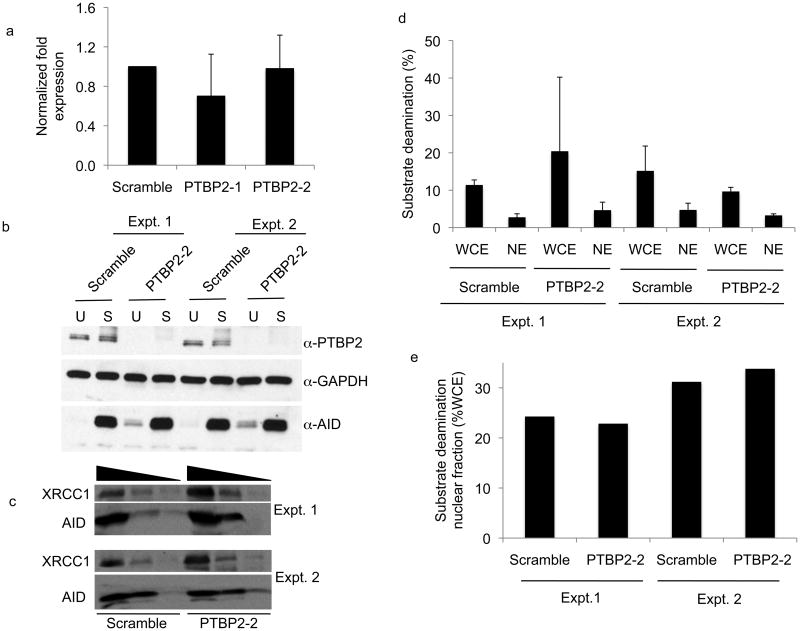
Figure 4.
AID expression and nuclear localization is not altered in PTBP2 knock-down cells. (a) AID mRNA expression in CIT-stimulated control or PTBP2 knock-down cells was quantified by reverse-transcription real-time quantitative PCR and normalized to β-actin. (b) Whole cell extracts (100 μg) derived from unstimulated (U) or CIT-stimulated (S) scramble or PTBP2-2 shRNA expressing cells were analyzed by immunoblots using indicated antibodies. Results from two independent knock-down experiments are shown. (c) Approximately 50 μg of nuclear protein from two independent PTBP2 knock-down experiments were analyzed by immunoblotting using AID and XRCC1 antibodies. XRCC1 served as a loading control for nuclear proteins. (d) Approximately 25 μg of whole cell (WCE) or nuclear (NE) extracts derived from two independent (Expt. 1, Expt. 2) PTBP2 knock-down or control cells were assayed for AID activity by measuring conversion of cytidine to uridine on a ssDNA substrate. Deamination was measured by the uracil release assay as described16. Deamination activity was plotted as a mean of three independent assays of each extract. Error-bars represent standard deviation from mean. (e) The fraction of nuclear AID activity was plotted as a percentage of total AID activity from the values obtained in panel (d).