Figure 2.
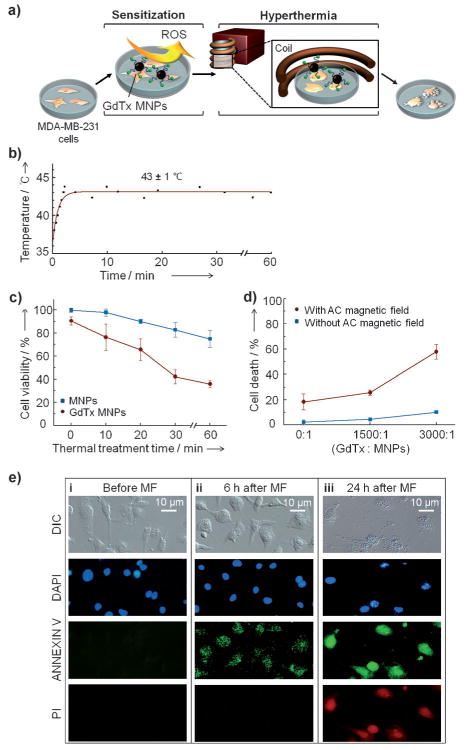
In vitro magnetic hyperthermia studies involving the GdTx MNPs and MDA-MB-231 cells. a) Illustration of the in vitro experiment. Briefly, GdTx MNP-treated MDA-MB-231 cells are incubated for 5 h and then an AC magnetic field is applied to effect hyperthermia. b) Temperature profile. A temperature of 43 ± 1 °C is maintained in an AC magnetic field of 37.4 kAm−1 at 500 kHz. c) Time dependence of the magnetic hyperthermia treatment effect. d) Dependence of the magnetic hyperthermia efficacy on GdTx loading level. e) Monitoring of MDA-MB-231 cell death pathway induced by magnetic hyperthermia using GdTx MNPs. Microscopic images of MDA-MB-231 cells before (i), and 6 h (ii) and 24 h (iii) after magnetic field (MF) application. In these experiments, the nuclei are stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue), and membrane inversion followed by membrane rupture is detected by annexin V-FITC (annexin V–fluorescein isothiocyanate;green) and propidium iodide (red, PI).
