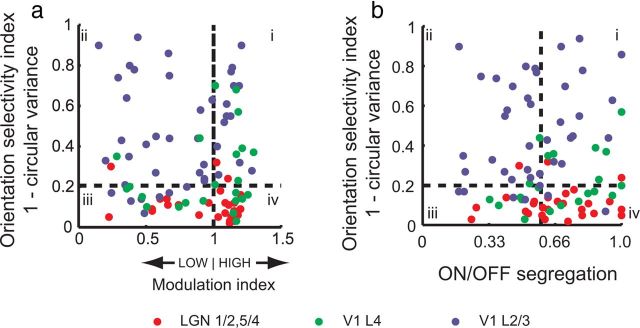
Figure 5.
Simple and complex cells in tree shrew V1. a, Orientation selectivity index plotted against the modulation index. To be considered simple, a cell's responses to drifting gratings must exhibit a modulation index of >1 and exhibit significant orientation selectivity (quadrant i; Skottun et al., 1991). By these criteria, several cells in V1 layers 4 and 2/3 can be classified as simple. Cells in quadrant ii are classic complex cells, and cells in quadrants iii and iv are unoriented. b, Orientation selectivity plotted against ON/OFF segregation index. The first investigators identified simple cells as those that exhibited both orientation selectivity and a spatial segregation of ON/OFF responses (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962). By this criteria, several cells among the cortical layer 4 and layer 2/3 cells in tree shrew would be classified as simple (quadrant i).