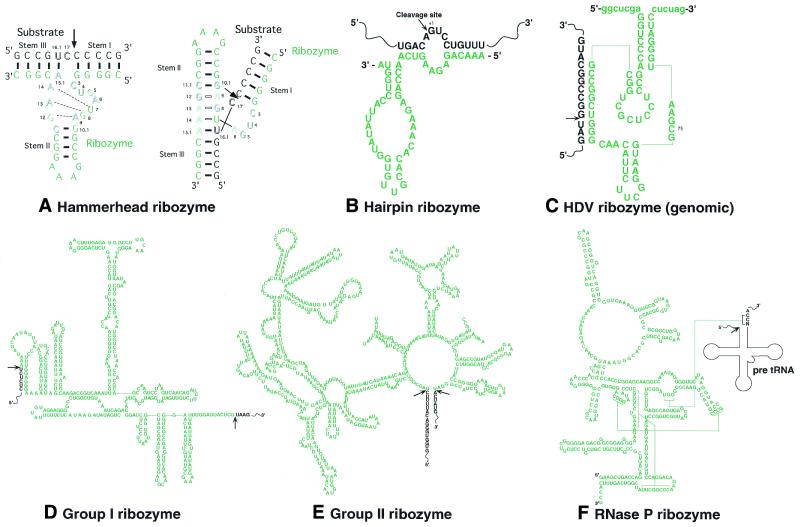
Figure 1.
The two-dimensional structures of various ribozymes. The ribozyme or intron portion is printed in green. The substrate or exon portion is printed in black. Arrows indicate sites of cleavage by ribozymes. (A) Left, the two-dimensional structure of a hammerhead ribozyme and its substrate. Outlined letters are conserved bases that are involved in catalysis. Right, the γ-shaped structure of the hammerhead ribozyme–substrate complex. (B–F) The two-dimensional structures of a hairpin ribozyme, the genomic HDV ribozyme, a group I ribozyme from Tetrahymena, a group II ribozyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (aiγ 5) and scherichiathe ribozyme of RNase P from E.coli, respectively.