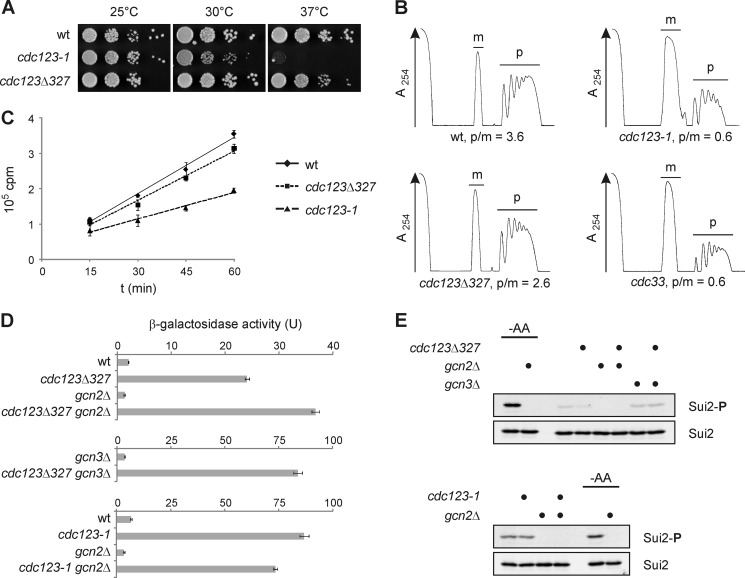
FIGURE 1.
Mutations in CDC123 affect translation initiation and eIF2 function. A, growth of cdc123 mutants. Cells were spotted in serial 10-fold dilutions on agar plates and incubated at the indicated temperatures. See supplemental Fig. S1 for cdc123 mutant alleles. B, polysome profiles of cdc123 mutants. Wild type cells (wt) and a strain expressing low levels of eIF4E (cdc33) were included for comparison. Strains were grown at 25 °C and shifted to 30 °C for 4 h prior to preparation of cell extracts. Monosomes (m) and polysomes (p) were separated in sucrose (10–50%) gradients, and their ratio (p/m) was quantified. RNA was measured at 254 nm (A254). C, global protein synthesis in cdc123 mutants. Wild type cells (wt) and cdc123 mutants were grown at 25 °C and shifted to 30 °C for 4 h prior to addition of [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine. Incorporation of radiolabeled amino acids into proteins was monitored over time. Shown are mean values and S.D. (n = 3). D, GCN4 expression in cdc123 mutants. GCN4-lacZ reporter levels were measured in strains of the indicated genotype. β-Galactosidase activity is shown as mean and S.D. (n = 3). E, eIF2α-ser52 phosphorylation in cdc123 mutants. An antibody to eIF2α-phospho-ser52 (Invitrogen, 44728G) was used to determine eIF2α phosphorylation (Sui2-P) by Western analysis. As a control, eIF2α-ser52 phosphorylation (Sui2-P) was induced by shifting cells to synthetic medium lacking amino acids (-AA) for 30 min. Total eIF2α levels (Sui2) were analyzed for comparison.