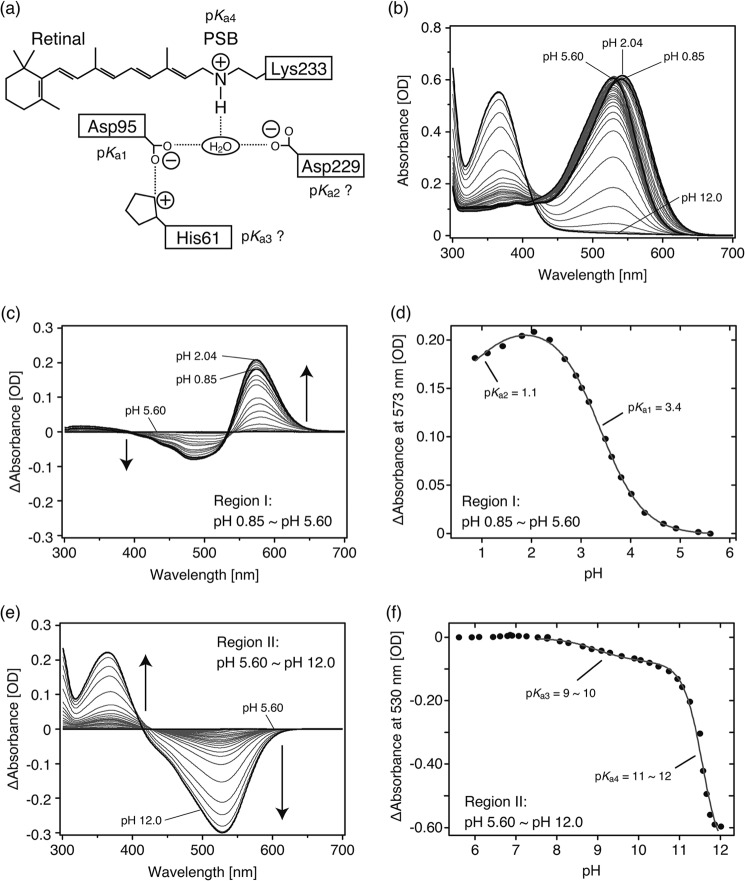
FIGURE 5.
pH-induced absorbance changes of TR. Purified TR was suspended in 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.0, 1 m NaCl, and 0.05% DDM. a, shown is a schematic illustration of the vicinity of the retinal chromophore based on the crystallographic structure of xanthorhodopsin (XR) (46). Four candidates, Asp-95, Asp-229, His-61, and the Schiff base, are represented that could influence the absorption spectra of TR. Symbols + and − denote positive and negative charges, respectively. The pKa values are tentatively assigned as shown. b, absorption spectra at various pH values are shown. Bold black lines represent the spectra at pH 5.60, where the spectrum was blue-shifted most, at pH 2.04, where the spectrum was red-shifted most, at pH 0.85, which is the end point for acidic pH, and at pH 12.0, which is the end point for alkaline pH. c and e, shown are difference spectra from pH 0.85 to pH 5.60 (Region I) (c) and from pH 5.60 to pH 12.0 (Region II) (e), respectively. The spectrum at pH 5.60 was subtracted from each spectrum and is described as a base line. In the pH range from 2.04 to 0.85, spectra were blue-shifted as indicated by the small decrease in absorption at 573 nm in the difference spectra (c). d and f, absorption differences at 573 nm (d) and at 530 nm (f) were plotted against pH ranging from 0.85 to 5.60 (Region I) and from 5.60 to 12.0 (Region II), respectively. The data in d were analyzed by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation with two pKa values (Equation 1) as described in the gray line. The data in f were partially analyzed by the same equation, but the fitting resulted in poor convergence. The estimated pKa values were as follows; pK1a1 = 3.4, pK1a2 = 1.1, pK1a3 = 9 ∼ 10, and pK1a4 = 11 ∼ 12.