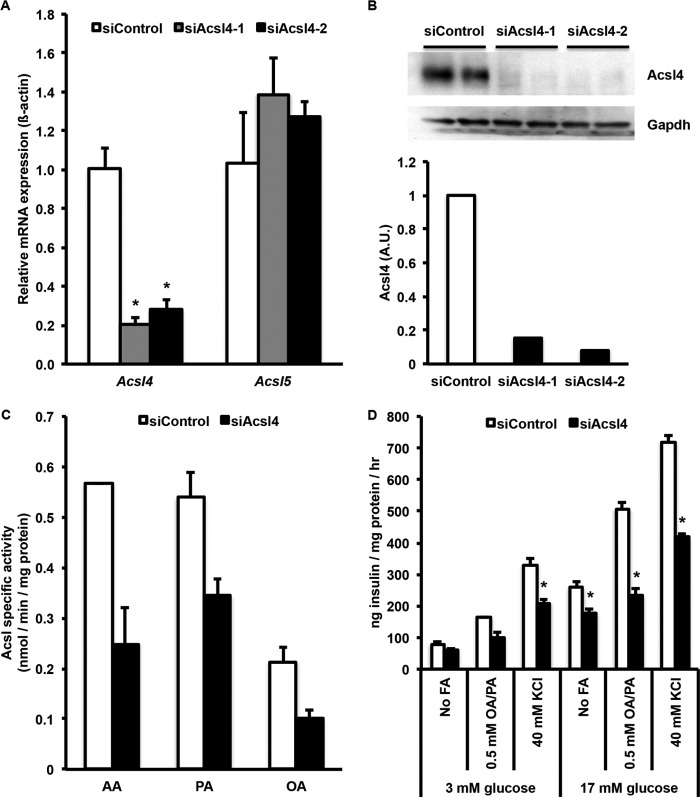
FIGURE 2.
Acsl4 siRNA knockdown in INS 832/13 cells reduced Acsl4 mRNA expression, Acsl4 protein expression, acyl-CoA synthetase activity, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, and fatty acid augmented insulin secretion. A, two separate siRNAs targeted against Acsl4 reduced mRNA expression by more than 75%. B, corresponding reduction of Acsl4 protein expression with Acsl4 siRNA knockdown by two independent Acsl4 siRNAs. Duplicate samples were examined with knockdown of >80% for each Acsl4 siRNA as quantified by densitometry relative to Gapdh loading control. A.U., arbitrary units. C, Acsl specific activity from siControl and siAcsl4-treated INS 832/13 cells with AA, palmitate (PA), and oleate (OA) as substrates. D, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion with or without KCl and fatty acid augmented insulin secretion with 2:1 oleate/palmitate (OA/PA) at the concentrations indicated. The results represent means ± S.E. of three separate experiments carried out at least in triplicate. *, p < 0.05 relative to siControl.