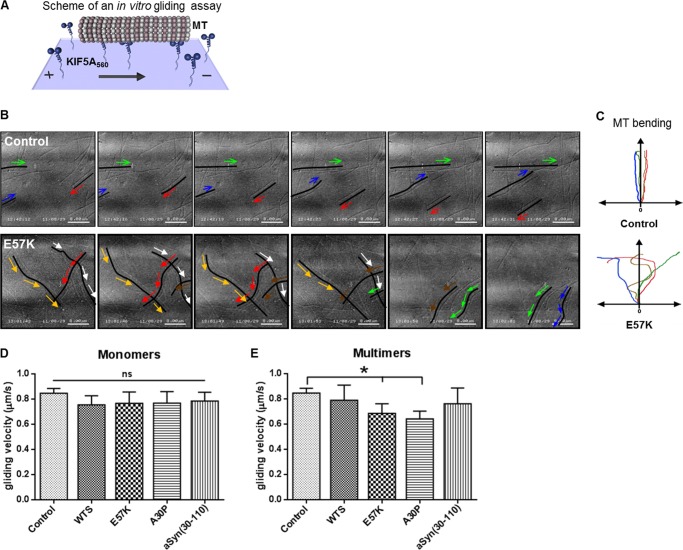
FIGURE 4.
MT gliding velocity in vitro is significantly impaired by α-Syn oligomers. A, in vitro gliding assays were performed using KIF5A560 and taxol-stabilized MTs in the presence of ATP. Monomeric or multimeric forms of WTS and α-Syn variants were added at a final concentration of 10 μm. The control gliding assay (Control) did not contain α-Syn. B, representative 3-s video sequences of a time lapse imaging of 19 s. Color arrows visualize movement directions of selected MTs that are visualized as black lines or curves. In a control condition, MTs were directed lines (Control; top), whereas MT movement was changing directions in the presence of oligomers (E57K; bottom). Respective representative videos are provided as supplemental material. C, a schematic summarizing MT gliding character in the absence (Control; top) and in the presence of α-Syn oligomers (E57K; bottom). The y axis shows a hypothetical MT movement direction, and color lines represent trajectories of individual MTs. D and E, mean gliding velocities ± S.D. (error bars) in the presence of WTS, α-Syn variants, and their multimers. Oligomers significantly reduced MT gliding velocity in vitro (E57K and A30P, respectively) (E). Three independent experiments were performed. Velocities of at least 10 MTs were measured in each experiment. *, p < 0.05; ns, not significant.