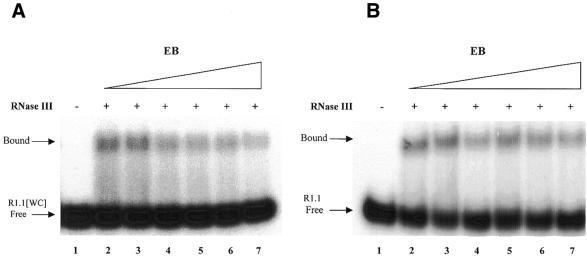
Figure 4.
Ethidium does not inhibit RNase III binding to substrate. Gel shift assays were carried out as described in Materials and Methods. (A) RNase III binding to R1.1[WC] RNA. 5′-32P-labeled RNA was combined with EB (concentrations given below), then RNase III was added (5 nM dimer concentration) and the sample electrophoresed in a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel (see Materials and Methods). The concentration of RNase III was chosen to provide only a partial shift, in order to provide maximal sensitivity to any inhibitory effect of EB. Higher concentrations of RNase III provide a complete shift of the free RNA to the bound form (data not shown). CaCl2 (10 mM) was included in the binding reactions and gel and electrophoresis buffers. The positions of bound and free R1.1[WC] RNA are indicated. The smear of radioactivity between free and bound RNA represents partial dissociation of the RNA–protein complex during electrophoresis, which has been noted elsewhere (37). Lane 1, no RNase III; lane 2, no EB; lane 3, 4 µM EB; lane 4, 12 µM EB; lane 5, 20 µM EB; lane 6, 40 µM EB; lane 7, 100 µM EB. (B) RNase III binding to R1.1 RNA. The same conditions as described above were used (10 mM CaCl2). Lane 1, no protein added; lane 2, no EB, lane 3, 4 µM EB; lane 4, 12 µM EB; lane 5, 20 µM EB; lane 6, 40 µM EB; lane 7, 80 µM EB.